Setting Up Replication Using VVR VEA
VVR VEA enables you to set up Volume Replicator (VVR) configurations on participating hosts from a remote client. VVR enables you to set up replication either when the data volumes are zero initialized or contain valid data, and when the application is active or stopped.
Before setting up a Replicated Data Set, lay out your VVR configuration using the Configuration Worksheet in the Volume Replicator Installation Guide. Follow the best practices or recommendations listed in Best Practices for Setting Up Replication to ensure successful configuration of VVR. You can set up replication using one of the following procedures:
The Create Replicated Data Set wizard guides you through the process of setting up replication using automatic synchronization. For instructions on setting up replication using the Create Replicated Data Set wizard, see Setting Up Replication Using the Create RDS Wizard. For instructions on setting up replication using separate tasks, see Setting Up Replication Using Individual Tasks.
Overview of Setting Up Replication
To configure and set up replication, the following tasks must be performed in the order presented below:
VVR VEA enables you to create a Primary RVG of an RDS using the Create Replicated Data Set wizard. Launch the wizard from the host that you want to be designated as the Primary in the RDS.
The Create Replicated Data Set wizard enables you to associate existing data volumes and the Storage Replicator Log (SRL) with the Primary RVG. The Create Replicated Data Set wizard performs the following operations:
- Creates the Primary RVG on the host to which you connected.
- Enables the Primary RVG by starting it.
- Associates the specified data volumes and Storage Replicator Log (SRL) with the RVG.
- Associates a Data Change Map (DCM) to each data volume in the RVG.
You can choose to add the Secondary using this wizard or add the Secondary later using the Add Secondary wizard.
You can choose to synchronize the Secondary later using the Synchronize Secondary wizard. Alternatively, you can synchronize the Secondary using the Start Replication dialog box and by choosing either Automatic Synchronization, Synchronization not needed, or Checkpoint options.
If an operation fails, a failure message lists the possible reasons of failure in the Result Details area. Read the details carefully and take appropriate corrective action. For more information about the error, note down the Unique Message Identifier (UMI) that is displayed with the error message, and then refer the VERITAS Technical Services knowledge base.
 Note
UMI is a string of the format "V-xx-yy-zz". For example, V-38-1-11 is the UMI displayed when an invalid Secondary host name is entered.
Note
UMI is a string of the format "V-xx-yy-zz". For example, V-38-1-11 is the UMI displayed when an invalid Secondary host name is entered.
Example Scenario
The instructions on how to use VVR VEA to set up a simple VVR configuration under different situations include examples. These examples explain how to set up a VVR configuration containing one Primary and one Secondary. Note that VVR VEA enables you to create and set up VVR configurations containing multiple Secondary hosts. The example configuration looks as follows:
Primary Host name: seattle
Disk group
|
hrdg
|
|---|
Primary RVG
|
hr_rvg
|
Primary RLINK to Secondary seattle
|
rlk_seattle_hr_rvg
|
Primary data volume #1
|
hr_dv01
|
Primary data volume #2
|
hr_dv02
|
Primary SRL volume
|
hr_srl
|
Secondary Host name: london
Disk group
|
hrdg
|
|---|
Secondary RVG
|
hr_rvg
|
Secondary RLINK to Primary london
|
rlk_london_hr_rvg
|
Secondary data volume #1
|
hr_dv01
|
Secondary data volume #2
|
hr_dv02
|
Secondary SRL volume
|
hr_srl
|
Setting Up Replication Using the Create RDS Wizard
The Create Replicated Data Set wizard guides you through the process of setting up replication using automatic synchronization.
 To set up replication using the Create Replicated Data Set wizard
To set up replication using the Create Replicated Data Set wizard
-
Launch the wizard from the host that you want to be designated as the Primary in the RDS.
-
Choose Replication > Create Replicated Data Set. To use the pop-up menu, right-click Replicated Data Sets and select Create Replicated Data Set Wizard.
-
In the Replicated Data Set Creation Wizard page, select Beginner User or Advanced User.
-
If you selected Advanced User, skip to step 6. If you selected Beginner User, the Important Prerequisites page is displayed.
-
In the Important Prerequisites page, click the check boxes and then click Next. Note that this page does not appear if you selected Advanced User in step 2. You cannot proceed if the data volumes and SRL of the same names and sizes do not exist on all the hosts in the RDS.
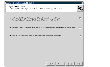
Click the thumbnail above to view full-sized image.
-
Complete the Assign a name to the Primary RVG page as follows:
Primary RVG Name
|
Enter the name of the Primary RVG. The name of the Primary RVG is designated as the name of the RDS. For example, hr_rvg.
|
Include VxVM ISP Volumes Only
|
Select this checkbox only if you want to include VxVM ISP (Intelligent Storage Provisioning) volumes in the RVG. You cannot include both VxVM ISP volumes and VxVM non-ISP volumes in the RVG.
|
After you have provided the required information, click Next.
-
Complete the Select the Disk Group and Data Volumes to be replicated page as follows:
Disk Group
|
Select the required disk group name from the drop-down list. For example, hrdg.
|
Data Volumes
|
Select the names of the data volumes by holding down the SHIFT key and clicking the names of the volumes you want to select. For example, hr_dv01, hr_dv02. Note that volumes with the same names must be created on the Primary host and all Secondary hosts. If you selected Include VxVM ISP Volumes Only, the list displays VxVM ISP volumes only.
|
After you have provided the required information, click Next.
-
In the Select the Replication Log page, select the name of the SRL, for example, hr_srl, and then click Next. If you selected Include VxVM ISP Volumes Only, the list displays VxVM ISP volumes only.
-
In the Summary Information for Creating the Primary Replicated Volume Group page, select Create Primary RVG after reviewing the information. If the operation of creating Primary RVG was successful, the next page displays a message that indicates that the Primary RVG has been created successfully.
If the operation fails, a failure message lists the possible reasons of failure in the Result Details area. Read the details carefully and take appropriate corrective action. For more information about the error, note down the Unique Message Identifier (UMI) that is displayed with the error message, and then refer the VERITAS Technical Services knowledge base.
 Note
UMI is a string of the format "V-xx-yy-zz". For example, V-38-1-11 is the UMI displayed when an invalid Secondary host name is entered.
Note
UMI is a string of the format "V-xx-yy-zz". For example, V-38-1-11 is the UMI displayed when an invalid Secondary host name is entered.
-
To add the Secondary now, click the Do you want to add Secondary? check box. If you want to add the Secondary later, click Finish.
-
Complete the Add Secondary Wizard page as follows:
| Hostname/IP Address for Replication
|
Primary
|
Enter a host name or specify the IP address that can be used for replication. The Primary host name must be resolvable and reachable from the Secondary host. For example, seattle. If you entered the IP address, it must be reachable from the Secondary host. The Replication IP column in the Secondary RVG view displays the value of the Primary host.
|
Secondary
|
Enter a host name or specify the IP address that can be used for replication. The Secondary host name must be resolvable and reachable from the Primary host. For example, london. If you entered the IP address, it must be reachable from the Primary host. The Replication IP column in the Primary RVG view displays the value of the Secondary host.
|
Replication Setting
|
The default values for Replication Mode, SRL Protection, and Protocol are displayed. You can keep the default or change these replication settings. To change the replication settings, click Advanced. The Advanced Settings dialog box appears.
|
-
To change the replication settings, complete the Advanced Settings dialog box as follows, or go to the next step.
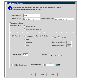
Click the thumbnail above to view full-sized image.
Secondary DG
|
If the name of the Secondary disk group is other than the default, enter the correct Secondary disk group name. This disk group must contain the SRL and data volumes that are to be associated with the Secondary RVG that is being created.
|
Primary RLINK
|
Enter the new Primary RLINK name if the default name is not appropriate.
|
Secondary RLINK
|
Enter the new Secondary RLINK name if the default name is not appropriate.
|
Replication Settings
|
Replication Mode
|
Asynchronous is selected by default. Select the required mode of replication. To enable synchronous mode, select Synchronous-Override. To set the replication mode to synchronous=fail, use the command-line interface. For more information, refer to Administering VERITAS Volume Replicator.
|
SRL Protection
AutoDCM, DCM, Override, Off
|
By default, SRL protection is set to AutoDCM. Select the required value to change the SRL protection mode. To enable SRL protection, select AutoDCM, DCM, or Override. To disable SRL protection, select Off. If you disable SRL protection, the SRL is allowed to overflow. To set the SRL protection mode to fail, use the command-line interface (CLI). For details on using the CLI, refer to Administering VERITAS Volume Replicator.
|
Latency Protection
Override, Off
|
By default, latency protection is set to Off. To enable latency protection and limit the number of updates by which the Secondary is allowed to fall behind, select Override. If you select Override, the wizard displays the boxes Latency Low Mark and Latency High Mark with default values of 9950 and 10000 respectively.
To disable latency protection, select Off.
To set the latency protection to fail, use the command-line interface (CLI). For details on using the CLI, refer to Administering VERITAS Volume Replicator.
|
If Latency Protection is set to Override:
|
Latency High Mark
|
Displays only if Latency Protection is set to Override. The default is 10000. Enter the required numerical limit.
|
Latency Low Mark
|
Displays only if Latency Protection is set to Override. The default is 9950. Enter the required numerical limit.
|
Packet Size
|
The default is 8400. Enter the required packet size.
|
Protocol
|
UDP is selected by default. Select UDP or TCP.
|
Set Bandwidth Limit
|
To control the network bandwidth to be used by VVR for replication, click the Set Bandwidth Limit check box; then specify the bandwidth limit. Note that the specified bandwidth limit must be greater than 56 kilo bits per second (kbps).
To disable Bandwidth Throttling, clear the Set Bandwidth Limit check box. This sets the bandwidth limit to none. By default, Bandwidth Throttling is disabled.
|
-
Select OK, and then select Add Secondary.
-
In the next page, the message indicates that the Secondary has been added successfully. If the operation of adding Secondary RVG was successful the page displays a success message.
If the operation fails, the page displays the failure message and lists the possible reasons of failure in the Result Details area. Read the details carefully and take appropriate corrective action. For more information about the error, note down the Unique Message Identifier (UMI) that is displayed with the error message, and then refer the VERITAS Technical Services knowledge base.
-
Select Do you want to synchronize Secondary? to synchronize the Secondary using automatic synchronization; otherwise, to quit the wizard, click Finish.
-
In the Synchronize Secondary Using Automatic Synchronization page, select Synchronize, and then select Finish.
| Note:
|
|---|
- To add more volumes after creating the RVG, use the Associate Volume task.
| |
Setting Up Replication Using Individual Tasks
To configure and set up replication without completely following through the Create Replicated Data Set wizard, perform the following discrete tasks:
Creating a Replicated Data Set
To create a Replicated Data Set (RDS) using VVR VEA, perform the following tasks in the order listed below:
Creating a Primary RVG of the RDS
Prerequisites for creating a Primary RVG:
 Data volumes of the same names and size must exist on all the hosts that are to be a part of the RDS.
Data volumes of the same names and size must exist on all the hosts that are to be a part of the RDS.
 SRLs of the same name must exist on all the hosts that are to be a part of the RDS.
SRLs of the same name must exist on all the hosts that are to be a part of the RDS.
 To create a Primary RVG of an RDS
To create a Primary RVG of an RDS
-
Perform step 1 to step 9 in Setting Up Replication Using the Create RDS Wizard.
-
Click Finish to create the Primary RVG of the RDS and quit the Create Replicated Data Set wizard.
Adding a Secondary to the RDS
 To add a Secondary to the RDS
To add a Secondary to the RDS
-
From the tree view, select the name of the RDS for which you want to create the Secondary. For example, hr_rvg.
-
Choose Replication > Add Secondary. To use the pop-up menu, right-click the name of the RDS, for example, seattle. The Add Secondary Wizard is displayed.
-
Click Next.
-
Perform step 11 to step 14 in Setting Up Replication Using the Create RDS Wizard.
-
Click Finish to add the Secondary to the RDS.
Synchronizing the Secondary and Starting Replication
Before starting replication, the Secondary data volumes must be synchronized with the Primary data volumes. The Start Replication task enables you to synchronize the Secondary and start replication between the Primary and a specific Secondary of an RDS.
The Start Replication task can be launched from any host in an RDS. The name of the RVG on the local host represents the RDS.
To synchronize the Secondary and start replication:
-
Select the name of the Secondary that is to be synchronized and to which you want to start replication. For example, london.
-
Choose Replication > Start Replication. The Start Replication Dialog Box is displayed.
Start Replication dialog box
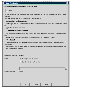
Click the thumbnail above to view full-sized image.
Start Replication Dialog Box
The Start Replication task provides the following options to start replication:
Starting Replication Using Automatic Synchronization
The instructions in this section assume that the RDS has been created using the procedure described in the section Creating a Replicated Data Set.
 To synchronize the Secondary and start replication using automatic synchronization
To synchronize the Secondary and start replication using automatic synchronization
-
Select the name of the Secondary that is to be synchronized and to which you want to start replication. For example, london.
-
Choose Replication > Start Replication. To use the pop-up menu, right-click the name of the Secondary, for example, london. The Start Replication dialog box is displayed.
-
From the Start Replication dialog box, select Automatic Synchronization and click OK. The Start Replication dialog box displays the result of your request to start replication.
| Notes:
|
|---|
- While automatic synchronization is in progress, the Replicated Data Set View for the RDS displays the Data Status as inconsistent, and the Replication Status as resync in progress (autosync).
- After the automatic synchronization completes, the Data Status changes to consistent; up-to-date and the Replication Status changes to replicating (connected) in the Replicated Data Set View for the RDS.
| |
Setting Up Replication Using Checkpoint
The instructions in this section assume that the RDS has been created using the procedure described in the section Creating a Replicated Data Set. You can synchronize the Secondary using block-level backup and checkpoint when the application is active or inactive.
-
Start a checkpoint using the command-line interface. For instructions, see Creating Checkpoints.
-
Perform a block-level backup of the data volumes in the Primary RVG.
-
End the checkpoint using the command-line interface.
-
Restore the backup to the Secondary data volumes.
-
Check whether the checkpoint you created is still valid by selecting the Checkpoints tab in the Primary RVG view and then clicking Get Checkpoints. If the checkpoint has overflowed, repeat step 1 to step 6.
-
Choose Replication > Start Replication to start replication. The Start Replication dialog box is displayed.
-
From the Start Replication dialog box, select Checkpoint to synchronize the Secondary and start replication using checkpoint.
-
From the drop-down box, select the name of the checkpoint.
-
Click OK. The Start Replication dialog box displays the result of your request to start replication.
-
Click OK to close the Results dialog box. The RDS View for hr_rvg on seattle is automatically refreshed to display the replication status at a particular point in time, for the replication that has just been started. If the Secondary is consistent, the synchronization was successful.
If the checkpoint overflows before the Secondary becomes consistent, the synchronization fails. Increase the size of the SRL, and then repeat step 1 to step 11. For instructions on resizing the SRL, see Resizing the SRL.
-
In the RDS view, check Data Status to find out whether the Secondary is up to date.
| Notes:
|
|---|
- The same backup and the corresponding checkpoint can be used to set up additional Secondary hosts while the checkpoint is still valid.
- If a checkpoint has overflowed, its corresponding backup cannot be used to resynchronize the Secondary using that checkpoint. Eventually, any checkpoint becomes STALE and unusable.
- While synchronization using checkpoint is in progress, the Replicated Data Set View for the RDS displays the Data Status as inconsistent, and the Replication Status as replicating (connected).
- After the synchronization using checkpoint completes, the Data Status changes to consistent and the Replication Status changes to replicating (connected) in the Replicated Data Set View for the RDS.
| |
Starting Replication When Data Volumes are Initialized with Zeroes
Because the Primary data volumes are initialized with zeroes, the data on the Secondary node does not need to be synchronized with the Primary. However, we recommend that you zero initialize the Secondary data volumes.
The instructions in this section assume that the RDS has been created using the procedure described in the section Creating a Replicated Data Set.
 Note
Do not start the application or mount the file system before completing step 4.
Note
Do not start the application or mount the file system before completing step 4.
-
Select the Secondary host name from the tree, and then choose Replication > Start Replication.
-
From the Start Replication dialog box, select Synchronization not needed.
-
Click OK. The Start Replication dialog box displays the result of your request to start replication.
-
Click OK to close the Start Replication dialog box.
-
Start the application.
| Notes:
|
|---|
- When this task is initiated, the Replicated Data Set View for the RDS displays the Data Status as consistent, and the Replication Status as replicating (connected).
- When this task completes, the Replicated Data Set View for the RDS displays the Data Status as consistent, and the Replication Status as replicating (connected).
| |
|


