Release 2 (9.2)
Part Number A96573-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle Advanced Security Administrator's Guide Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96573-01 |
|
This chapter describes how to configure Oracle Advanced Security for Oracle9i, or for the Oracle9i server, so that CyberSafe TrustBroker, a Kerberos-based authentication server, can be used to authenticate Oracle users. This chapter contains the following topics:
To configure CyberSafe authentication:
Perform this task on the system that functions as the authentication server.
| See Also:
CyberSafe documentation listed under Related Documentation |
Perform this task on the system that runs the Oracle database server and the client.
| See Also:
CyberSafe documentation listed under Related Documentation |
Perform this task on both the client and server systems.
| See Also:
CyberSafe documentation listed under Related Documentation |
For the Oracle database server to validate the identity of clients, configure a service principal for an Oracle database server on the system running the CyberSafe TrustBroker Master Server. If required, also configure a realm.
The name of the principal has the following format:
kservice/kinstance@REALM
The field values in the service principal name are described in Table 5-1.
|
Note: The utility names in this section are executable programs. However, the CyberSafe user name CYBERUSER and the realm |
For example, if the Oracle service is oracle, the fully-qualified name of the system on which Oracle is running is dbserver.someco.com, and the realm is SOMECO.COM, the principal name is:
oracle/dbserver.someco.com@SOMECO.COM
Run kdb5_edit as root to create the service principal as follows:
# cd /krb5/admin# ./kdb5_edit
To add a principal named oracle/dbserver.someco.com@SOMECO.COM to the list of server principals known by CyberSafe, enter the following in kdb5_edit:
kdb5_edit: ark oracle/dbserver.someco.com@SOMECO.COM
Extract a service table from CyberSafe and copy it to both the Oracle database server and CyberSafe TrustBroker client systems.
For example, to extract a service table for dbserver.someco.com, perform the following steps.
kdb5_edit:
kdb5_edit: xst dbserver.someco.com oracle 'oracle/dbserver.someco.com@SOMECO.COM' added to keytab 'WRFILE:dbserver.someco.com-new-srvtab'kdb5_edit: exit# /krb5/bin/klist -k -t dbserver.someco.com-new-srvtab
If you do not enter a realm (SOMECO.COM in the example) when using xst, kdb5_edit uses the realm of the current host and displays it in the command output, as shown in the proceeding input example.
# mv dbserver.someco.com-new-srvtab /krb5/v5srvtab
If the service table is on a different system from the CyberSafe TrustBroker client, transfer the file with a program such as FTP. If using FTP, transfer the file in binary mode.
/krb5/v5srvtab). Set the file owner to the Oracle user, or make the file readable by the group to which Oracle belongs. Do not make the file readable to all users--this can enable a security breach.Install an Oracle database server on the same system that is running the CyberSafe TrustBroker client.
Install CyberSafe, along with Oracle Advanced Security, during a custom installation of Oracle9i. The Oracle Universal Installer guides you through the entire installation process.
Configure Oracle Net and Oracle9i on both the server and client systems.
Perform the following tasks to set parameters in the Oracle database server and client sqlnet.ora files to configure CyberSafe:
(init.ora).To configure CyberSafe authentication service parameters on both the client and the database server:
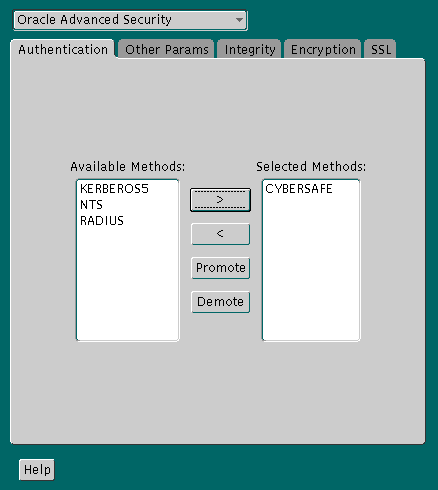
Text description of the illustration cyb0001.gif
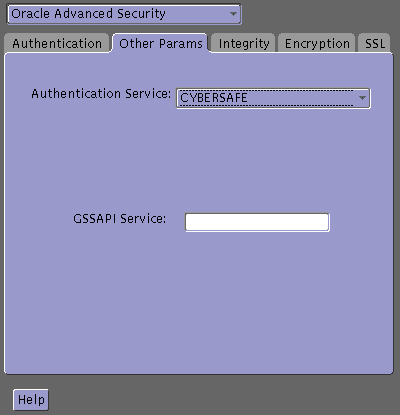
oracle/dbserver.someco.com @SOMECO.COM
Insert the principal name, using the format described in Task 4: Configure a Service Principal for an Oracle Database Server.
The sqlnet.ora file is updated with the following entries:
SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES=(CYBERSAFE)SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_GSSAPI_SERVICE=KSERVICE/KINSTANCE@REALM
Add the following parameter to the Initialization Parameter File (init.ora):
REMOTE_OS_AUTHENT=FALSE
Because CyberSafe user names can be long, and Oracle user names are limited to 30 characters, Oracle Corporation recommends using null for the value of
OS_AUTHENT_PREFIX, as follows:
OS_AUTHENT_PREFIX=""
Restart the Oracle database server after modifying the configuration files to enable the changes.
| See Also:
Oracle operating system-specific documentation and Oracle9i Database Administrator's Guide for more information about how to restart the Oracle database server |
For CyberSafe to authenticate Oracle users, you must create them on the CyberSafe authentication server where the administration tools are installed. The following steps assume that the realm already exists.
|
Note: The utility names in this section are executable programs. However, the CyberSafe user name CYBERUSER and realm |
Run /krb5/admin/kdb5_edit as root on the authentication server to create the new CyberSafe user, such as CYBERUSER.
Enter the following:
# kdb5_editkdb5_edit:ank cyberuserEnter password:<password>(password does not display)Re-enter password for verification:<password>(password does not display)kdb5_edit: quit
| See Also:
Cybersafe documentation listed in Related Documentation for information about creating the realm |
Run SQL*Plus to create the Oracle user, and enter the following commands on the Oracle database server (note that the Oracle user name must be uppercase and enclosed in double quotation marks):
In this example, OS_AUTHENT_PREFIX is set to null ("").
SQL> CONNECT / AS SYSDBA;SQL> CREATE USER "CYBERUSER@SOMECO.COM" IDENTIFIED EXTERNALLY;SQL> GRANT CREATE SESSION TO "CYBERUSER@SOMECO.COM";
Before users can connect to the database, they must run kinit on the clients for an initial ticket:
% kinit cyberuser
% klist
The system displays the following information:
| Creation Date | Expiration Date | Service |
|---|---|---|
|
11-Aug-99 16:29:51 |
12-Aug-99 00:29:21 |
krbtgt/SCMECO.COM@SOMECO.COM |
|
11-Aug-99 16:29:51 |
12-Aug-99 00:29:21 |
oracle/dbserver.someco.com@SOMECO.COM |
After running kinit to get an initial ticket, users can connect to an Oracle database server without using a user name or password. Enter a command similar to the following:
% sqlplus /@net_service_name
where net_service_name is a Oracle Net service name.
For example:
% sqlplus /@npddoc_db
| See Also:
Chapter 1, Introduction to Oracle Advanced Security, and Oracle9i Heterogeneous Connectivity Administrator's Guide |
This section describes some common configuration problems and explains how to resolve them:
|
 Copyright © 1996, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|