How Data Flows in an RDS Containing Multiple Secondary Hosts
This section explains how VVR processes an incoming write for a Replicated Data Set (RDS) containing multiple Secondary hosts, some replicating in asynchronous mode and some in synchronous mode.
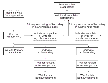
How Data Flows in an RDS with Multiple Secondaries
Click the thumbnail above to view full-sized image.
In asynchronous and synchronous mode of replication, VVR processes an incoming write as follows:
-
Receives a write from the application.
-
Writes it to the SRL.
-
Sends the write to the Secondary hosts replicating in synchronous mode and in asynchronous mode. At the same time, VVR writes to the data volume on the Primary.
-
On the Secondary, VVR receives the write, processes it, and sends a network acknowledgement to the Primary.
-
When the Primary receives a network acknowledgement from the Secondary hosts replicating in synchronous mode, VVR acknowledges to the application that the write is complete.
Note that the Secondary RVG sends the network acknowledgement as soon as the write is received in the VVR kernel memory. This removes the time required to write to the Secondary data volumes from the application latency. On the Primary, VVR waits only for the network acknowledgement from all the synchronous Secondary hosts and not for the data to be written to the Secondary data volumes. This improves application performance. However, VVR tracks all such acknowledged writes that have not been written to the data volumes. VVR can replay these tracked writes if the Secondary crashes before writing to the data volumes on the Secondary or if the Primary crashes before receiving the data acknowledgement.
-
When the write is written to the data volumes on the Secondary, VVR sends a data acknowledgement from the Secondary to the Primary in both synchronous and asynchronous mode.
-
When the Primary receives the data acknowledgement from all the Secondary hosts, VVR marks the write as complete in the SRL.
|
