| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96540-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96540-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
Use the ASSOCIATE STATISTICS statement to associate a statistics type (or default statistics) containing functions relevant to statistics collection, selectivity, or cost with one or more columns, standalone functions, packages, types, domain indexes, or indextypes.
For a listing of all current statistics type associations, query the USER_ASSOCIATIONS data dictionary view. If you analyze the object with which you are associating statistics, then you can also query the associations in the USER_USTATS view.
| See Also:
ANALYZE for information on the order of precedence with which |
To issue this statement, you must have the appropriate privileges to alter the base object (table, function, package, type, domain index, or indextype). In addition, unless you are associating only default statistics, you must have execute privilege on the statistics type. The statistics type must already have been defined.
| See Also:
CREATE TYPE for information on defining types |
associate_statistics::=
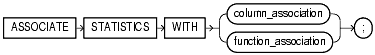
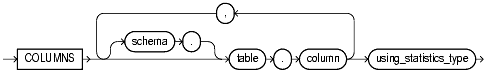
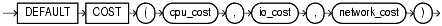

Specify one or more table columns. If you do not specify schema, then Oracle assumes the table is in your own schema.
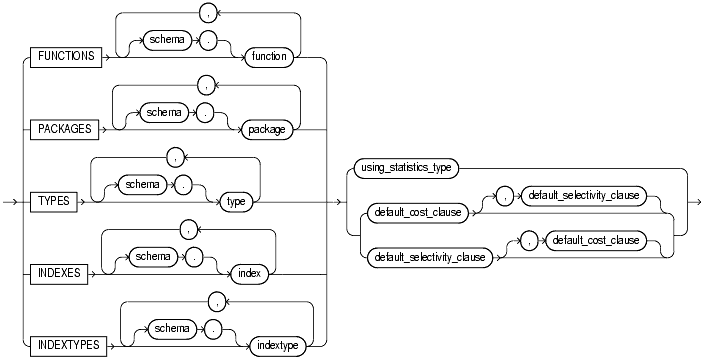
Specify one or more standalone functions, packages, user-defined datatypes, domain indexes, or indextypes. If you do not specify schema, then Oracle assumes the object is in your own schema.
FUNCTIONS refers only to standalone functions, not to method types or to built-in functions.TYPES refers only to user-defined types, not to built-in SQL datatypes.You cannot specify an object for which you have already defined an association. You must first disassociate the statistics from this object.
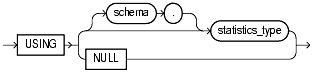
Specify the statistics type (or a synonym for the type) being associated with column, function, package, type, domain index, or indextype. The statistics_type must already have been created.
The NULL keyword is valid only when you are associating statistics with a column or an index. When you associate a statistics type with an object type, columns of that object type inherit the statistics type. Likewise, when you associate a statistics type with an indextype, index instances of the indextype inherit the statistics type.You can override this inheritance by associating a different statistics type for the column or index. Alternatively, if you do not want to associate any statistics type for the column or index, then you can specify NULL in the using_statistics_type clause.
You cannot specify NULL for functions, packages, types, or indextypes.
| See Also:
Oracle9i Data Cartridge Developer's Guide for information on creating statistics collection functions |
Specify default costs for standalone functions, packages, types, domain indexes, or indextypes. If you specify this clause, then you must include one number each for CPU cost, I/O cost, and network cost, in that order. Each cost is for a single execution of the function or method or for a single domain index access. Accepted values are integers of zero or greater.
Specify as a percent the default selectivity for predicates with standalone functions, types, packages, or user-defined operators. The default_selectivity must be a number between 0 and 100. Values outside this range are ignored.
You cannot specify DEFAULT SELECTIVITY for domain indexes or indextypes.
This statement creates an association for the standalone package emp_mgmt (created in "Creating a Package: Example"):
ASSOCIATE STATISTICS WITH PACKAGES emp_mgmt DEFAULT SELECTIVITY 10;
This statement specifies that using the domain index t_a to implement a given predicate always has a CPU cost of 100, I/O of 5, and network cost of 0.
ASSOCIATE STATISTICS WITH INDEXES t_a DEFAULT COST (100,5,0);
The optimizer will simply use these default costs instead of calling a cost function.