Release 2 (9.2)
Part Number A96621-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle9i XML Developer's Kits Guide - XDK Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96621-01 |
|
This chapter describes the JavaBeans available for use with Oracle XML. The topics in this chapter are:
The Oracle XML Transviewer beans are provided as part of XDK for JavaBeans with the Oracle9i Enterprise and Standard Editions from Release 2 (8.1.6) and higher. If you do not have these editions, then you can download the beans from the site: http://otn.oracle.com/tech/xml
XML Transviewer Beans facilitate the addition of graphical interfaces to your XML applications.
Bean encapsulation includes documentation and descriptors that can be accessed directly from Java Integrated Development Environments like JDeveloper.
A sample application that demonstrates all of the beans to create a simple XML editor and XSL transformer is included with your software.
The included sample application with the XML SQL Utility (XSU) cause the following:
Database Connectivity is included with the XML Transviewer Beans. The beans can now connect directly to a JDBC-enabled database to retrieve and store XML and XSL files.
XML Transviewer Beans comprises the following beans:
The DOMBuilder bean is a non-visual bean. It builds a DOMTree from an XML document.
The DOMBuilder bean encapsulates the XML Parser for Java's DOMParser class with a bean interface and extends its functionality to permit asynchronous parsing. By registering a listener, Java applications can parse large or successive documents and then allow control to return immediately to the caller.
The XSLTransformer bean is a non-visual bean. It accepts an XML file, applies the transformation specified by an input XSL stylesheet and creates the resulting output file.
XSLTransformer bean enables you to transform an XML document to almost any text-based format including XML, HTML, and DDL, by applying the appropriate XSL stylesheet.
The Treeviewer bean displays XML formatted files graphically as a tree. The branches and leaves of this tree can be manipulated with a mouse.
The XMLSourceView bean is a visual Java bean. It allows visualization of XML documents and editing. It enables the display of XML and XSL formatted files with color syntax highlighting when modifying an XML document with a text editor. This helps view and edit the files. It can be integrated with DOMBuilder bean, and allows pre- or post-parsing visualization and validation against a specified DTD.
This is a visual Java bean that applies XSL transformations on XML documents and shows the results. It allows editing of XML and XSL input files.
DBViewer bean is Java bean that displays database queries or any XML by applying XSL stylesheets and visualizing the resulting HTML in a scrollable swing panel. DBViewer bean has XML and XSL tree buffers as well as a result buffer. DBViewer bean allows the calling program to:
The result can be stored in the result buffer. The XML and XSL buffer content can be shown as a source or tree structure. The result buffer content can be rendered as HTML and also shown as source or tree structure. The XML buffer can be loaded from a database query.
DBAccess bean maintains CLOB tables that contain multiple XML and text documents.
The guidelines for using the XML Transviewer Beans are described in the following sections:
DOMBuilder() class implements an XML 1.0 parser according to the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) recommendation. It parses an XML document and builds a DOM tree. The parsing is done in a separate thread and the DOMBuilderListener interface must be used for notification when the tree is built.
The DOMBuilder bean encapsulates the XML Parser for Java with a bean interface. It extends its functionality to permit asynchronous parsing. By registering a listener, a Java application can parse documents and return control return to the caller.
Asynchronous parsing in a background thread can be used interactively in visual applications. For example, when parsing a large file with the normal parser, the user interface freezes until the parsing has completed. This can be avoided with the DOMBuilder bean. After calling the DOMBuilder bean parse method, the application can immediately regain control and display "Parsing, please wait". If a "Cancel" button is included you can also cancel the operation. The application can continue when domBuilderOver() method is called by DOMBuilder bean when background parsing task has completed.
When parsing a large number of files, DOMBuilder bean can save time. Response times that are up to 40% faster have been recorded when compared to parsing the files one by one.
Figure 10-1 illustrates DOMBuilder Bean usage.
DOMBuilder.addDOMBuilderListener(DOMBuilderListener) and adds DOMBuilderListener.| See Also :
Table 10-1 for a list of available methods to apply |
DOMBuilderOver() method. This is called when it receives an asynchronous call from an application. This interface must be implemented to receive notifications about events during asynchronous parsing. The class implementing this interface must be added to the DOMBuilder using addDOMBuilderListener method.
Available DOMBuilderListener methods are:
DOMBuilder.getDocument() fetches the resulting DOM document and outputs the DOM document.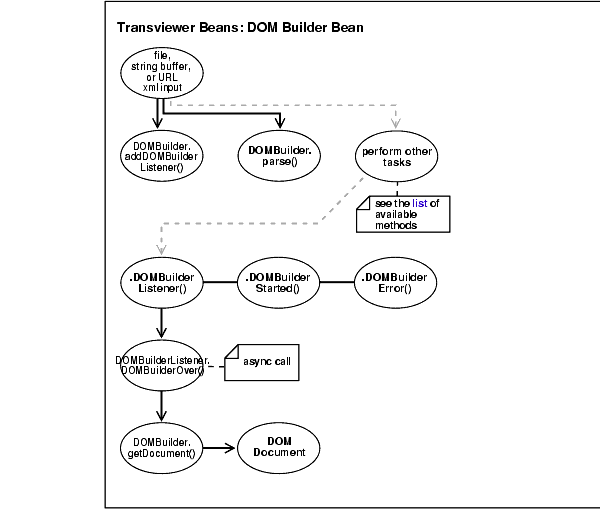
The XSLTransformer bean accepts an XML file and applies the transformation specified by an input XSL stylesheet to create and output file. It enables you to transform an XML document to almost any text-based format including XML, HTML, and DDL, by applying an XSL stylesheet.
When integrated with other beans, XSLTransformer bean enables an application or user to immediately view the results of transformations.
This bean can also be used as the basis of a server-side application or servlet to render an XML document, such as an XML representation of a query result, into HTML for display in a browser.
The XSLTransformer bean encapsulates the Java XML Parser XSLT processing engine with a bean interface and extends its functionality to permit asynchronous transformation.
By registering a listener, your Java application can transform large and successive documents by having the control returned immediately to the caller.
XSL transformations can be time consuming. Use XSL Transformer bean in applications that transform large numbers of files and it can concurrently transform multiple files.
XSLTransformer bean can be used for visual applications for a responsive user interface. There are similar issues here as with DOMBuilder bean.
By implementing XSLTransformerListener() method, the caller application can be notified when the transformation is complete. The application is free to perform other tasks in between requesting and receiving the transformation.
This scenario illustrates one way of applying XSLTransformer bean.
The HTML stored in the CLOB table always mirrors the last data stored in the tables being queried. A JSP (Java Server Page) can display the HTML.
In this scenario, multiple end users do not produce multiple data queries that contribute to larger loads to the database. The HTML is regenerated only when the underlying data changes.
Figure 10-2 illustrates XSLTransformer bean usage. For examples of implementing this bean, see "Transviewer Bean Example 1: AsyncTransformSample.java".
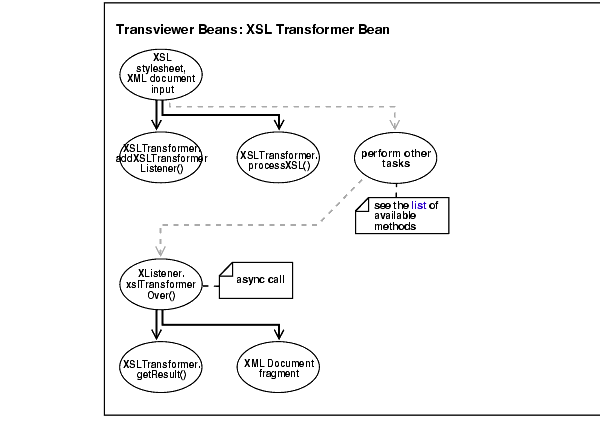
XSLTransfomer.addXSLTransformerListener(XSLTransformerListener)method. This adds a listener.XSLTransformerListener.xslTransformerOver() method is called. This interface must be implemented to receive notifications about events during the asynchronous transformation. The class implementing this interface must be added to the XSLTransformer event queue using the method addXSLTransformerListener.The Treeviewer bean displays an XML document as a tree. It recognizes the following XML DOM nodes:
It takes as input an org.w3c.dom.Document object.
Figure 10-3, "Treeviewer Bean in Action: Displaying an XML Document as a Tree" shows how the Treeviewer bean displays the XML document and the editing options.
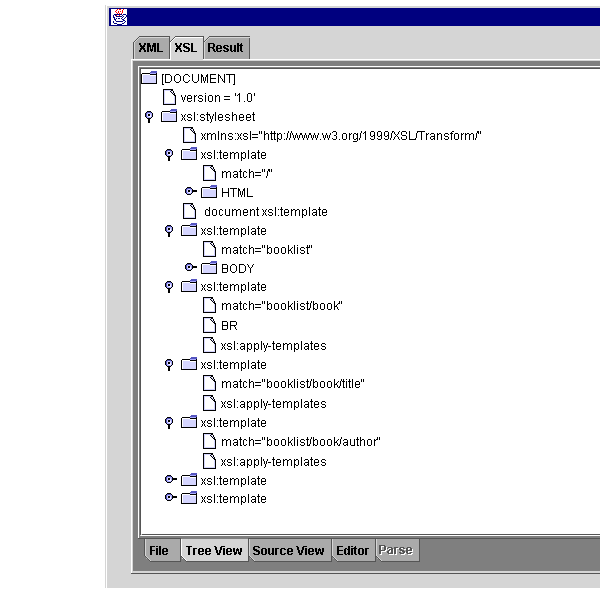
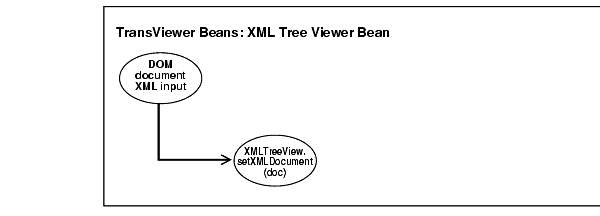
Figure 10-4 illustrates XML Treeviewer bean usage. A DOM XML document is input to the XMLTreeView.setXMLDocument(doc) method. This associates the XML Treeviewer with the XML document. The Treeviewer bean methods are:
XMLSourceView bean is a visual Java bean that displays an XML document. It improves the viewing of XML and XSL files by color-highlighting the XML/XSL syntax. It also offers an Edit mode. XMLSourceView bean easily integrates with DOMBuilder bean. It allows for pre- or post-parsing visualization and validation against a specified DTD.
XMLSourceView bean recognizes the following XML token types:
Each token type has a foreground color and font. The default color/font settings can be changed by the user. This takes an org.w3c.dom.Document object as input.
Figure 10-5 displays an XML document with tags shown in blue, tag content in black, and attributes in red.
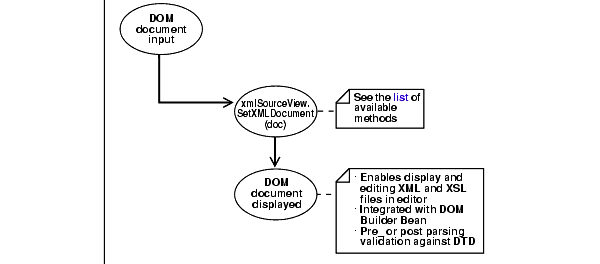
Figure 10-6 shows the XMLSourceView bean usage. This is part of the oracle.xml.srcviewer API. A DOM document inputs XMLSourceView.SetXMLDocument(Doc). The resulting DOM document is displayed. See "Transviewer Bean Example 2: ViewSample.java".
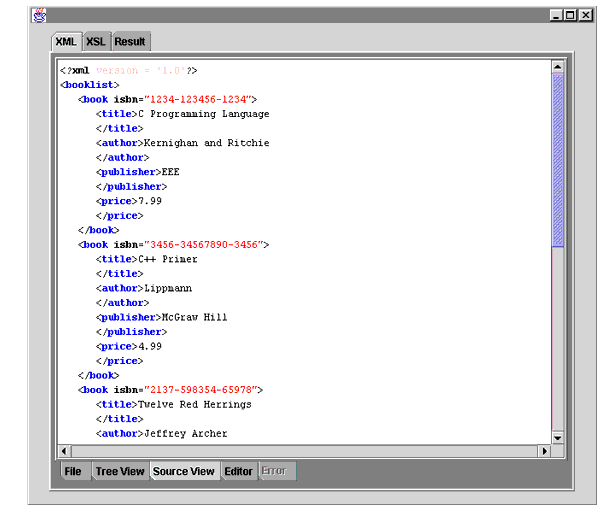
The following table, Table 10-3, lists the XMLSourceView Bean methods.
XMLTransformPanel visual bean applies XSL transformations to XML documents. It visualizes the result and allows editing of input XML and XSL documents and files. XMLTransformPanel bean requires no programmatic input. It is a component that interacts directly with you and is not customizable.
XMLTransformPanel bean has the following features:
|
Note: CLOB tables created by the XSL Transformer bean can be used by trigger-based stored procedures to mirror tables or views in the database into HTML data held in these CLOB tables. See "XSL Transviewer Bean Scenario 1: Regenerating HTML Only When Data Changes". |
The Transviewer bean is one application that illustrates the use of XMLTransform Panel bean. It can be used from a command line to perform the following actions:
| See Also:
"Transviewer Bean Example 3: XMLTransformPanelSample.java" for an example of how to use XMLTransformPanel. |
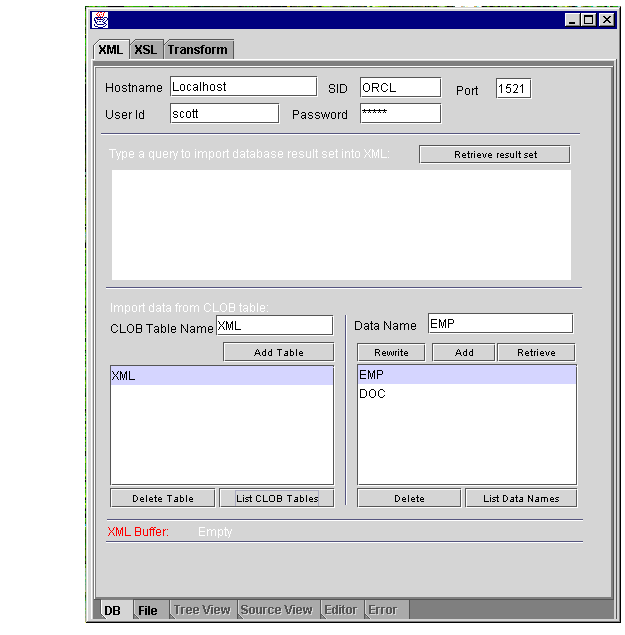
DBViewer bean can be used to display database queries on any XML document by applying XSL stylesheets and visualizing the resulting HTML in a scrollable swing panel. See:
DBViewer bean has the following three buffers:
DBViewer bean API allows the calling program to load or save buffers from various sources and apply stylesheet transformation to the XML buffer using the stylesheet in the XSL buffer. Results can be stored in the result buffer.
Content in the XML and XSL buffers can be shown as a source or tree structure. Content in the result buffer can be rendered as HTML and also shown as a source or tree structure.
The XML buffer can be loaded using a database query. All the buffers can be loaded from and files saved from the following:
Therefore, control can also be used to move files between the file system and the user schema in the database.
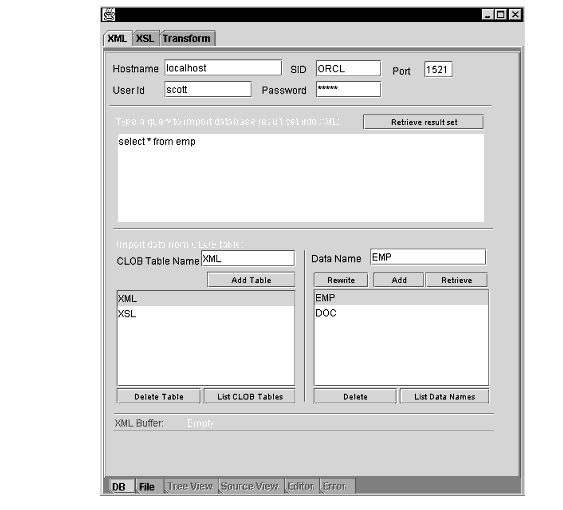
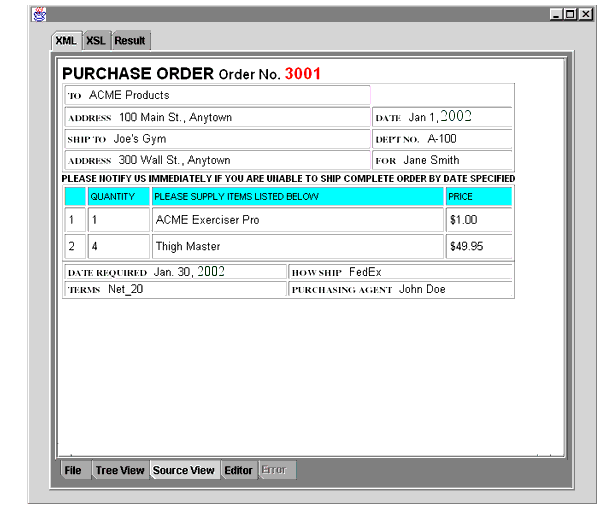
Figure 10-10 illustrates DBViewer bean's usage.
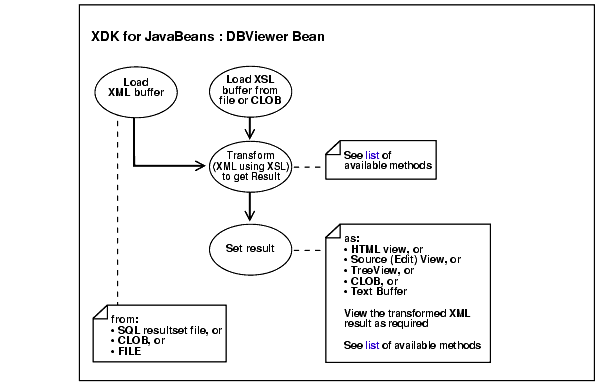
Table 10-4 lists the DBViewer bean methods.
DBAccess bean maintains CLOB tables that can hold multiple XML and text documents. Each table is created using the following statement:
CREATE TABLE tablename FILENAME CHAR( 16) UNIQUE, FILEDATA CLOB) LOB(FILEDATA) STORE AS (DISABLE STORAGE IN ROW)
Each XML (or text) document is stored as a row in the table. The FILENAME field holds a unique string used as a key to retrieve, update, or delete the row. Document text is stored in the FILEDATA field. This is a CLOB object. CLOB tables are automatically maintained by the Transviewer bean. The CLOB tables maintained by DBAccess bean can be later used by the Transviewer bean. DBAccess bean does the following tasks:
Figure 10-11 illustrates the DBAccess bean usage. It shows how DBAccess bean maintains, and manipulates XML documents stored in CLOBs.
Table 10-5 lists the DBAccess bean methods.
The XML Diff Bean performs a tree comparison on two XML DOM trees. It displays the two XML trees and shows the differences between the XML trees. A node can be inserted, deleted, moved, or modified. Each of these operations is shown in a different color or style as in the following list:
Moves will be displayed visually as a delete or insert operation.
You can generate the differences between the two XML trees in the form of XSL code. The first XML file can be transformed into the second XML file by using the XSL code generated.
The XMLDiff Bean has the methods described in this section.
Finds the differences between the two XML files or the two XMLDocument objects.
Implements the DOMBuilderErrorListener interface called only by the DOM parser.
Implements the DOMBuilderErrorListener interface called only by the DOM parser when there is an error while parsing.
Implements the DOMBuilderListener interface called only by a DOM parser thread when the parsing is done.
Implements the DOMBuilderListener interface called only by the DOM parser when the parsing begins.
Performs the comparison of two nodes. It is called by the differ algorithm. You can overwrite this function for customized comparisons.
Generates an XSL stylesheet as an XMLDocument that initially represents the differences between the two XML document sets.
Generates an XSL file of input filename that represents the differences between the two XML files which were initially set.
Gets the text panel as JTextPane object that visually shows the diffs in the first XML file.
Gets the text panel as a JTextPane object that visually shows the diffs in the second XML file or document.
Gets the document root as an XMLDocument object of the first XML tree
Gets the document root as an XMLDocument object of the second XML tree
Prints the diff tree that contains the node names and values that have been identified as diffs by the algorithm. This method is useful for debugging.
Sets the XML documents which need to be compared.
Sets the XML files which need to be compared.
Sets the indentation for the XSL generation. This should be called before the generateXSLFile() or generateXSLDoc() methods. The indentation will be applied to all attributes only. For indenting newly inserted nodes besides attributes see void setNewNodeIndentIncr(int spaces).
Sets the first XML file that needs to be compared.
Sets the first XML document that needs to be compared.
Sets the second XML file that needs to be compared.
Sets the second XML document that needs to be compared.
Sets the indentation for the XSL generation. This should be called before the generateXSLFile() or generateXSLDoc() methods. The indentation will be applied to all newly inserted nodes only (except attributes). For attributes indentation support see void setIndentIncr(int spaces).
Assumes that there are no moves to be detected by the diff algorithm. This function should be called before the diff() function. Using this method should improve performance.
The XDK for Java Transviewer bean sample/ directory contains sample Transviewer bean applications that illustrate how to use Oracle Transviewer beans. Oracle Transviewer beans toolset contains DOMBuilder, XMLSourceView, XMLTreeView, XSLTransformer, XMLTransformPanel, DBViewer, DBAccess, and XMLDiff beans.
Table 10-6 lists the sample files in sample/.
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
booklist.xml |
Sample XML file used by Example 1, 2, or 3. |
|
doc.xml |
Sample XML file used by Example 1, 2, or 3. |
|
doc.html |
Sample HTML file used by Examples 1, 2, or 3. |
|
doc.xsl |
Sample input XSL file used by Examples 1, 2, or 3. doc.xsl is used by XSLTransformer. |
|
emptable.xsl |
Sample input XSL file used by Examples 1, 2, or 3. |
|
tohtml.xsl |
Sample input XSL file used by Examples 1, 2, or 3. Transforms booklist.xml. |
|
See "Transviewer Bean Example 1: AsyncTransformSample.java". |
Sample nonvisual application using XSLTransformer bean and DOMBuilder bean. It applies the XSLT stylesheet specified in doc.xsl on all *.xml files from the current directory. The results are in the files with extension.log. |
|
Sample visual application that uses XMLSourceView and XMLTreeView beans.It visualizes XML document files. |
|
|
See "Transviewer Bean Example 3: XMLTransformPanelSample.java". |
A visual application that uses XMLTransformPanel bean. This bean uses all four beans from above. It applies XSL transformations on XML documents and shows the result Visualizes and allows editing of XML and XSL input files. |
|
See: |
A sample visual application that uses DBViewer bean to implement simple insurance claim handling application. |
|
A sample visual application by which users can graphically compare any two XML files. The differences between the two files can be viewed as XSLT code. The first XML file can be transformed into the second XML file using the generated XSLT. |
The Transviewer beans require as a minimum JDK 1.1.6, and can be used with any version of JDK 1.2.
After installing this components, include classes111.zip and oraclexmlsql.jar in your classpath.
Makefile to point to your JDK path. In addition, on Windows NT, change the file separator as stated in the Makefile. If you do not have an ORACLE_HOME set, then set it to the root directory of your XDK JavaBeans installation.Use the sample files XMLDiffData1.txt and XMLDiffData2.txt to test the demo sample6 for the XMLDiff Bean. A few .xml files are provided as test cases. An XSL stylesheet 'doc.xsl' is used by XSLTransformer.
|
Note: sample1 runs the XMLTransViewer program so that you can import and export XML files from Oracle9i, keep your XSL transformation files in Oracle9i, and apply stylesheets to XML interactively. |
To use the database connectivity feature in this program, you must know the following:
You also need an account with CREATE TABLE privilege.
You can try the default account scott with password tiger if it still enabled on your Oracle9i system.
The following is the makefile script:
# Makefile for sample java files .SUFFIXES : .java .class CLASSES = ViewSample.class AsyncTransformSample.class XMLTransformPanelSample.class # Change it to the appropriate separator based on the OS PATHSEP= : # Change this path to your JDK location. If you use JDK 1.1, you will need # to download also Swing 1.1 and add swingall.jar to your classpath. # You do not need to do this for JDK 1.2 since Swing is part of JDK 1.2 JDKPATH = /usr/local/packages/jdk1.2 # Make sure that the following product jar/zip files are in the classpath: # - Oracle JDBC driver for thin client (file classes111.zip) # - Oracle XML SQL Utility (file oraclexmlsql.jar) # You can download this products from technet.us.oracle.com # CLASSPATH :=$(CLASSPATH)$(PATHSEP)../lib/xmlparserv2.jar$(PATHSEP)../lib/xmlcomp.jar$(PATH SEP)../lib/jdev-rt.zip$(PATHSEP).$(PATHSEP) %.class: %.java $(JDKPATH)/bin/javac -classpath "$(CLASSPATH)" $< # make all class files all: $(CLASSES) sample1: XMLTransformPanelSample.class $(JDKPATH)/bin/java -classpath "$(CLASSPATH)" XMLTransformPanelSample sample2: ViewSample.class $(JDKPATH)/bin/java -classpath "$(CLASSPATH)" ViewSample sample3: AsyncTransformSample.class $(JDKPATH)/bin/java -classpath "$(CLASSPATH)" AsyncTransformSample
This example shows you how to use DOMBuilder and the XSLTransformer beans to asynchronously transform multiple XML files.
import java.net.URL; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.Vector; import org.w3c.dom.DocumentFragment; import org.w3c.dom.DOMException; import oracle.xml.async.DOMBuilder; import oracle.xml.async.DOMBuilderEvent; import oracle.xml.async.DOMBuilderListener; import oracle.xml.async.DOMBuilderErrorEvent; import oracle.xml.async.DOMBuilderErrorListener; import oracle.xml.async.XSLTransformer; import oracle.xml.async.XSLTransformerEvent; import oracle.xml.async.XSLTransformerListener; import oracle.xml.async.XSLTransformerErrorEvent; import oracle.xml.async.XSLTransformerErrorListener; import oracle.xml.async.ResourceManager; import oracle.xml.parser.v2.DOMParser; import oracle.xml.parser.v2.XMLDocument; import oracle.xml.parser.v2.XSLStylesheet; import oracle.xml.parser.v2.*; public class AsyncTransformSample { /** * uses DOMBuilder bean */ void runDOMBuilders () { rm = new ResourceManager (numXMLDocs); for (int i = 0; i < numXMLDocs; i++) { rm.getResource(); try { DOMBuilder builder = new DOMBuilder(i); URL xmlURL = createURL(basedir + "/" + (String)xmlfiles.elementAt(i)); if (xmlURL == null) exitWithError("File " + (String)xmlfiles.elementAt(i) + " not found"); builder.setPreserveWhitespace(true); builder.setBaseURL (createURL(basedir + "/")); builder.addDOMBuilderListener (new DOMBuilderListener() { public void domBuilderStarted(DOMBuilderEvent p0) {} public void domBuilderError(DOMBuilderEvent p0) {} public synchronized void domBuilderOver(DOMBuilderEvent p0) { DOMBuilder bld = (DOMBuilder)p0.getSource(); runXSLTransformer (bld.getDocument(), bld.getId()); } }); builder.addDOMBuilderErrorListener (new DOMBuilderErrorListener() { public void domBuilderErrorCalled(DOMBuilderErrorEvent p0) { int id = ((DOMBuilder)p0.getSource()).getId(); exitWithError("Error occurred while parsing " + xmlfiles.elementAt(id) + ": " + p0.getException().getMessage()); } }); builder.parse (xmlURL); System.err.println("Parsing file " + xmlfiles.elementAt(i)); } catch (Exception e) { exitWithError("Error occurred while parsing " + (String)xmlfiles.elementAt(i) + ": " + e.getMessage()); } } } /** * uses XSLTransformer bean */ void runXSLTransformer (XMLDocument xml, int id) { try { XSLTransformer processor = new XSLTransformer (id); XSLStylesheet xsl = new XSLStylesheet (xsldoc, xslURL); processor.showWarnings (true); processor.setErrorStream (errors); processor.addXSLTransformerListener (new XSLTransformerListener() { public void xslTransformerStarted (XSLTransformerEvent p0) {} public void xslTransformerError(XSLTransformerEvent p0) {} public void xslTransformerOver (XSLTransformerEvent p0) { XSLTransformer trans = (XSLTransformer)p0.getSource(); saveResult (trans.getResult(), trans.getId()); } }); processor.addXSLTransformerErrorListener (new XSLTransformerErrorListener() { public void xslTransformerErrorCalled(XSLTransformerErrorEvent p0) { int i = ((XSLTransformer)p0.getSource()).getId(); exitWithError("Error occurred while processing " + xmlfiles.elementAt(i) + ": " + p0.getException().getMessage()); } }); processor.processXSL (xsl, xml); // transform xml document } catch (Exception e) { exitWithError("Error occurred while processing " + xslFile + ": " + e.getMessage()); } } void saveResult (DocumentFragment result, int id) { System.err.println("Transforming '" + xmlfiles.elementAt(id) + "' to '" + xmlfiles.elementAt(id) + ".log'" + " applying '" + xslFile); try { File resultFile = new File((String)xmlfiles.elementAt(id) + ".log"); ((XMLNode)result).print(new FileOutputStream(resultFile)); } catch (Exception e) { exitWithError("Error occurred while generating output : " + e.getMessage()); } rm.releaseResource(); } void makeXSLDocument () { System.err.println ("Parsing file " + xslFile); try { DOMParser parser = new DOMParser(); parser.setPreserveWhitespace (true); xslURL = createURL (xslFile); parser.parse (xslURL); xsldoc = parser.getDocument(); } catch (Exception e) { exitWithError("Error occurred while parsing " + xslFile + ": " + e.getMessage()); } } private URL createURL(String fileName) throws Exception { URL url = null; try { url = new URL(fileName); } catch (MalformedURLException ex) { File f = new File(fileName); try { String path = f.getAbsolutePath(); // This is a bunch of weird code that is required to // make a valid URL on the Windows platform, due // to inconsistencies in what getAbsolutePath returns. String fs = System.getProperty("file.separator"); if (fs.length() == 1) { char sep = fs.charAt(0); if (sep != '/') path = path.replace(sep, '/'); if (path.charAt(0) != '/') path = '/' + path; } path = "file://" + path; url = new URL(path); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { exitWithError("Cannot create url for: " + fileName); } } return url; } boolean init () throws Exception { File directory = new File (basedir); String[] dirfiles = directory.list(); for (int j = 0; j < dirfiles.length; j++) { String dirfile = dirfiles[j]; if (!dirfile.endsWith(".xml")) continue; xmlfiles.addElement(dirfile); } if (xmlfiles.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("No files in directory were selected for processing"); return false; } numXMLDocs = xmlfiles.size(); return true; } private void exitWithError(String msg) { PrintWriter errs = new PrintWriter(errors); errs.println(msg); errs.flush(); System.exit(1); } void asyncTransform () throws Exception { System.err.println (numXMLDocs + " XML documents will be transformed" + " using XSLT stylesheet specified in " + xslFile + " with " + numXMLDocs + " threads"); makeXSLDocument (); runDOMBuilders (); // wait for the last request to complete while (rm.activeFound()) Thread.sleep(100); } String basedir = new String ("."); OutputStream errors = System.err; Vector xmlfiles = new Vector(); int numXMLDocs = 1; String xslFile = new String ("doc.xsl"); URL xslURL; XMLDocument xsldoc; private ResourceManager rm; /** * main */ public static void main (String args[]) { AsyncTransformSample inst = new AsyncTransformSample(); try { if (!inst.init()) System.exit(0); inst.asyncTransform (); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.exit(0); } }
This example shows you how to use XMLSourceView and XMLTreeView beans to visually represent XML files.
import java.awt.*; import oracle.xml.srcviewer.*; import oracle.xml.treeviewer.*; import oracle.xml.parser.v2.XMLDocument; import oracle.xml.parser.v2.*; import org.w3c.dom.*; import java.net.*; import java.io.*; import java.util.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.event.*; public class ViewSample { public static void main(String[] args) { String fileName = new String ("booklist.xml"); if (args.length > 0) { fileName = args[0]; } JFrame frame = setFrame ("XMLViewer"); XMLDocument xmlDocument = getXMLDocumentFromFile (fileName); XMLSourceView xmlSourceView = setXMLSourceView (xmlDocument); XMLTreeView xmlTreeView = setXMLTreeView (xmlDocument); JTabbedPane jtbPane = new JTabbedPane (); jtbPane.addTab ("Source", null, xmlSourceView, "XML document sorce view"); jtbPane.addTab ("Tree", null, xmlTreeView, "XML document tree view"); jtbPane.setPreferredSize (new Dimension(400,300)); frame.getContentPane().add (jtbPane); frame.setTitle (fileName); frame.setJMenuBar (setMenuBar()); frame.setVisible (true); } static JFrame setFrame (String title) { JFrame frame = new JFrame (title); //Center the window Dimension screenSize = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize(); Dimension frameSize = frame.getSize(); if (frameSize.height > screenSize.height) { frameSize.height = screenSize.height; } if (frameSize.width > screenSize.width) { frameSize.width = screenSize.width; } frame.setLocation ((screenSize.width - frameSize.width)/2, (screenSize.height - frameSize.height)/2); frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { System.exit(0); } }); frame.getContentPane().setLayout (new BorderLayout()); frame.setSize(new Dimension(400, 300)); frame.setVisible (false); frame.setTitle (title); return frame; } static JMenuBar setMenuBar () { JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); JMenu menu = new JMenu ("Exit"); menu.addMenuListener ( new MenuListener () { public void menuSelected (MenuEvent ev) { System.exit(0); } public void menuDeselected (MenuEvent ev) {} public void menuCanceled (MenuEvent ev) {} }); menuBar.add (menu); return menuBar; } /** * creates XMLSourceView object */ static XMLSourceView setXMLSourceView(XMLDocument xmlDocument) { XMLSourceView xmlView = new XMLSourceView(); xmlView.setXMLDocument(xmlDocument); xmlView.setBackground(Color.yellow); xmlView.setEditable(true); return xmlView; } /** * creates XMLTreeView object */ static XMLTreeView setXMLTreeView(XMLDocument xmlDocument) { XMLTreeView xmlView = new XMLTreeView(); xmlView.setXMLDocument(xmlDocument); xmlView.setBackground(Color.yellow); return xmlView; } static XMLDocument getXMLDocumentFromFile (String fileName) { XMLDocument doc = null; try { DOMParser parser = new DOMParser(); try { String dir= "" ; FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(fileName); parser.setPreserveWhitespace(false); parser.setBaseURL(createURL(dir)); parser.parse(in); in.close(); } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); System.exit(0); } doc = (XMLDocument)parser.getDocument(); try { doc.print(System.out); } catch (Exception ie) { ie.printStackTrace(); System.exit(0); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return doc; } static URL createURL(String fileName) { URL url = null; try { url = new URL(fileName); } catch (MalformedURLException ex) { File f = new File(fileName); try { String path = f.getAbsolutePath(); String fs = System.getProperty("file.separator"); if (fs.length() == 1) { char sep = fs.charAt(0); if (sep != '/') path = path.replace(sep, '/'); if (path.charAt(0) != '/') path = '/' + path; } path = "file://" + path; url = new URL(path); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { System.out.println("Cannot create url for: " + fileName); System.exit(0); } } return url; } }
This example is an interactive application that uses XMLTransformPanel bean to do the following:
import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; import oracle.xml.transviewer.XMLTransformPanel; public class XMLTransformPanelSample { XMLTransformPanel transformPanel = new XMLTransformPanel(); /** * Adjust frame size and add transformPanel to it. */ public XMLTransformPanelSample () { Frame frame = new JFrame(); Dimension screenSize = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize(); frame.setSize(510,550); transformPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(510,550)); Dimension frameSize = frame.getSize(); if (frameSize.height > screenSize.height) { frameSize.height = screenSize.height; } if (frameSize.width > screenSize.width) { frameSize.width = screenSize.width; } frame.setLocation ((screenSize.width - frameSize.width)/2, (screenSize.height - frameSize.height)/2); frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { System.exit(0); } }); frame.setVisible(true); ((JFrame)frame).getContentPane().add (transformPanel); frame.pack(); } /** * main(). Only creates XMLTransformPanelSample object. */ public static void main (String[] args) { new XMLTransformPanelSample (); } }
This is an interactive example which lets you input the name or policy of an insurance claim. The appropriate claim is loaded as an XML buffer from the result set of an XML query. An XSL stylesheet is loaded from the file system. The DBViewer bean transforms the XML buffer using the XSL stylesheet to HTML. This HTML output can then be viewed.
import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import oracle.jdeveloper.layout.*; import oracle.xml.dbviewer.*; public class DBViewClaims extends JPanel { DBViewer dbPanel= new DBViewer(); JButton searchButton = new JButton(); XYLayout xYLayout1 = new XYLayout(); JLabel titleLabel = new JLabel(); JLabel nameLabel = new JLabel(); JLabel policyLabel = new JLabel(); JTextField nameTF = new JTextField(); JTextField policyTF = new JTextField(); JButton viewXMLButton = new JButton(); JButton viewXSLButton = new JButton(); JButton viewHTMLButton = new JButton(); public DBViewClaims() { super(); try { jbInit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void jbInit() throws Exception { setBackground(SystemColor.controlLtHighlight); this.setLayout(xYLayout1); searchButton.setText("searchButton"); searchButton.setLabel("Search"); xYLayout1.setHeight(464); xYLayout1.setWidth(586); titleLabel.setText("List of Claims"); titleLabel.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER); titleLabel.setBackground(new Color(192, 192, 255)); titleLabel.setFont(new Font("Dialog", 1, 16)); nameLabel.setText("Last Name"); policyLabel.setText("Policy:"); viewXMLButton.setText("viewXMLButton"); viewXMLButton.setLabel("view XML"); viewXMLButton.addActionListener(new java.awt.event.ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { viewXMLButton_actionPerformed(e); } }); viewXSLButton.setText("viewXSLButton"); viewXSLButton.setLabel("view XSL"); viewXSLButton.addActionListener(new java.awt.event.ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { viewXSLButton_actionPerformed(e); } }); viewHTMLButton.setText("viewHTMLButton"); viewHTMLButton.setLabel("view HTML"); viewHTMLButton.addActionListener(new java.awt.event.ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { viewHTMLButton_actionPerformed(e); } }); searchButton.addActionListener(new java.awt.event.ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { searchButton_actionPerformed(e); } }); this.add(dbPanel, new XYConstraints(16, 55, 552, 302)); this.add(searchButton, new XYConstraints(413, 415, 154, 29)); this.add(titleLabel, new XYConstraints(79, 10, 413, 31)); this.add(nameLabel, new XYConstraints(333, 373, 72, -1)); this.add(policyLabel, new XYConstraints(334, 395, 59, -1)); this.add(nameTF, new XYConstraints(413, 368, 155, -1)); this.add(policyTF, new XYConstraints(413, 391, 156, -1)); this.add(viewXMLButton, new XYConstraints(19, 359, 94, 29)); this.add(viewXSLButton, new XYConstraints(19, 390, 94, 29)); this.add(viewHTMLButton, new XYConstraints(19, 421, 94, 29)); updateUI(); } void searchButton_actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String sqlText="select * from s_claim c "; try { if (!nameTF.getText().equals("")) { sqlText=sqlText+" where c.claimpolicy.primaryinsured.lastname="+ "'"+nameTF.getText()+"'"; } else if (!policyTF.getText().equals("")) { sqlText=sqlText+" where c.claimpolicy.policyid="+ policyTF.getText(); } dbPanel.setUsername("scott"); dbPanel.setPassword("tiger"); dbPanel.setInstancename("orcl"); dbPanel.setHostname("localhost"); dbPanel.setPort("1521"); dbPanel.loadXMLBufferFromSQL(sqlText); dbPanel.loadXslBuffer("xslfiles","CLAIM.XSL"); dbPanel.transformToRes(); dbPanel.setResHtmlView(true); } catch (Exception e1) { System.out.println(e1); } } void viewXMLButton_actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { dbPanel.setXmlSourceEditView(true); } void viewXSLButton_actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { dbPanel.setXslSourceEditView(true); } void viewHTMLButton_actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { dbPanel.setResHtmlView(true); } }
This example provides a frame with a menu bar to access the DBView Claims functionality. Claims can then be loaded and displayed in HTML.
import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import oracle.jdeveloper.layout.*; public class DBViewFrame extends JFrame { JMenuBar menuBar1 = new JMenuBar(); JMenu menuFile = new JMenu(); JMenuItem menuFileExit = new JMenuItem(); JMenuItem menuListCustomerClaims = new JMenuItem(); public DBViewFrame() { super(); try { jbInit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void jbInit() throws Exception { this.getContentPane().setLayout(new GridLayout(1,1)); this.setSize(new Dimension(600, 550)); menuFile.setText("File"); menuFileExit.setText("Exit"); menuListCustomerClaims.setText("List Claims"); menuFileExit.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { fileExit_ActionPerformed(e); } }); menuListCustomerClaims.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { ListCustomerClaims_ActionPerformed(e); } }); menuFile.add(menuFileExit); menuFile.add(menuListCustomerClaims); menuBar1.add(menuFile); this.setJMenuBar(menuBar1); this.setBackground(SystemColor.controlLtHighlight); } void fileExit_ActionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { System.exit(0); } void ListCustomerClaims_ActionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { this.getContentPane().removeAll(); this.getContentPane().add(new DBViewClaims()); this.getContentPane().paintAll(this.getGraphics()); } }
This example simply provides a main function which instantiates DBViewFrame, giving it a specific look and feel.
import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; public class DBViewSample { public DBViewSample() { DBViewFrame frame = new DBViewFrame(); frame.setVisible(true); } public static void main(String[] args) { try { UIManager.setLookAndFeel(UIManager.getSystemLookAndFeelClassName()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } new DBViewSample(); } }
import oracle.xml.parser.v2.*; import oracle.xml.async.*; import oracle.xml.differ.*; import java.io.*; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.tree.*; import java.net.URL; import java.net.MalformedURLException; public class XMLDiffSample { /** * Constructor */ public XMLDiffSample() { } /** * main * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { dfxApp = new XMLDiffSample(); diffFrame = new XMLDiffFrame(dfxApp); diffFrame.addTransformMenu(); xmlDiff = new XMLDiff(); if (args.length == 3) outFile = args[2]; /* Use the default outFile name = XMLDiffSample.xsl */ if(args.length >= 2) dfxApp.showDiffs(new File(args[0]), new File(args[1])); diffFrame.setVisible(true); } public void showDiffs(File file1, File file2) { try { xmlDiff.setFiles(file1, file2); /* Check if files are equal */ if(!xmlDiff.diff()) { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(diffFrame, "Files are equivalent in XML representation", "XMLDiffSample Message", JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE); } /* generate xsl file */ xmlDiff.generateXSLFile(outFile); /* parse the xsl file created, alternately you can use generateXSLDoc to get the xsl as a document tree instead of a file */ parseXSL(); /* Display the document trees created by the xmlDiff object */ diffFrame.makeSrcPane(xmlDiff.getDocument1(), xmlDiff.getDocument2()); diffFrame.makeDiffSrcPane(new XMLDiffSrcView(xmlDiff.getDiffPane1()), new XMLDiffSrcView(xmlDiff.getDiffPane2())); diffFrame.makeXslPane(xslDoc, "Diff XSL Script"); diffFrame.makeXslTabbedPane(); }catch (FileNotFoundException e) { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(diffFrame, "File Not Found: "+e.getMessage(), "XMLDiffSample Error Message", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(diffFrame, "Error: "+e.getMessage(), "XMLDiffSample Error Message", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE); } } public void doXSLTransform() { try { doc1 = xmlDiff.getDocument1(); doc2 = xmlDiff.getDocument2(); XSLProcessor xslProc = new XSLProcessor(); /* Using the xsl stylesheet generated (xslDoc), transform the first file (doc1) into the second file (resultDocFrag) */ XMLDocumentFragment resultDocFrag = xslProc.processXSL(new XSLStylesheet (xslDoc, createURL(outFile)), doc1); XMLDocument resultDoc = new XMLDocument(); /* The XML declaration has to be copied over to the transformed XML doc, the xsl will not generate it automatically */ if (doc1.getFirstChild() instanceof XMLDeclPI) if (doc1.getFirstChild() instanceof XMLDeclPI) { XMLNode xmldecl = (XMLNode) resultDoc.importNode(doc1.getFirstChild(), false); resultDoc.appendChild(xmldecl); } /* Create the DTD node in the transformed XML document */ if(doc1.getDoctype() != null) { DTD dtd = (DTD)doc1.getDoctype(); resultDoc.setDoctype(dtd.getName(), dtd.getSystemId(), dtd.getPublicId()); } /* Create the result document tree from the document fragment */ resultDoc.appendChild(resultDocFrag); diffFrame.makeResultFilePane(resultDoc); } catch (XSLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(diffFrame, "Error: "+e.getMessage(), "XMLDiffSample Error Message", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(diffFrame, "Error:"+e.getMessage(), "XMLDiffSample Error Message", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE); } } /* Parse the XSL file generated into a DOM tree */ protected void parseXSL() { try { BufferedReader xslFile = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(outFile)); DOMParser domParser = new DOMParser(); domParser.parse(xslFile); xslDoc = domParser.getDocument(); }catch (FileNotFoundException e) { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(diffFrame, "File Not Found: "+e.getMessage(), "XMLDiffSample Message", JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE); } catch (Exception e) { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(diffFrame, "Error:"+e.getMessage(), "XMLDiffSample Error Message", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE); } } // create a URL from a file name protected URL createURL(String fileName) { URL url = null; try { url = new URL(fileName); } catch (MalformedURLException ex) { File f = new File(fileName); try { String path = f.getAbsolutePath(); // to handle Windows platform String fs = System.getProperty("file.separator"); if (fs.length() == 1) { char sep = fs.charAt(0); if (sep != '/') path = path.replace(sep, '/'); if (path.charAt(0) != '/') path = '/' + path; } path = "file://" + path; url = new URL(path); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(diffFrame, "Cannot create url for: " + fileName, "XMLDiffSample Error Message", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE); } } return url; } protected XMLDocument doc1; /* DOM tree for first file */ protected XMLDocument doc2; /* DOME tree for second file */ protected static XMLDiffFrame diffFrame; /* GUI frame */ protected static XMLDiffSample dfxApp; /* XMLDiff sample application */ protected static XMLDiff xmlDiff; /* XML diff object */ protected static XMLDocument xslDoc; /* parsed xsl file */ protected static String outFile = new String("XMLDiffSample.xsl"); /* output xsl file name */ }
import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import java.io.*; import javax.swing.*; import oracle.xml.parser.v2.*; import oracle.xml.srcviewer.*; import oracle.xml.differ.*; import org.w3c.dom.*; public class XMLDiffFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener { public XMLDiffFrame(XMLDiffSample dfApp) { super(); mydfApp = dfApp; init(); } public void makeSrcPane(XMLDocument doc1, XMLDocument doc2) { //undo srcviewer highlighting here XMLSourceView XmlSrcView1 = new XMLSourceView(); XmlSrcView1.setXMLDocument(doc1); XmlSrcView1.setTagForeground(Color.black); XmlSrcView1.setAttributeValueForeground(Color.black); XmlSrcView1.setPIDataForeground(Color.black); XmlSrcView1.setCommentDataForeground(Color.black); XmlSrcView1.setCDATAForeground(Color.black); XmlSrcView1.setBackground(Color.lightGray); XmlSrcView1.getJTextPane().setBackground(Color.white); XmlSrcView1.add(new JLabel(filename1,SwingConstants.CENTER), BorderLayout.NORTH); XMLSourceView XmlSrcView2 = new XMLSourceView(); XmlSrcView2.setXMLDocument(doc2); XmlSrcView2.setTagForeground(Color.black); XmlSrcView2.setAttributeValueForeground(Color.black); XmlSrcView2.setPIDataForeground(Color.black); XmlSrcView2.setCommentDataForeground(Color.black); XmlSrcView2.setCDATAForeground(Color.black); XmlSrcView2.setBackground(Color.lightGray); XmlSrcView2.getJTextPane().setBackground(Color.white); XmlSrcView2.add(new JLabel(filename2,SwingConstants.CENTER), BorderLayout.NORTH); XmlSrcView2.updateUI(); XmlSrcView1.updateUI(); srcPane = new JSplitPane(JSplitPane.HORIZONTAL_SPLIT, XmlSrcView1, XmlSrcView2); srcPane.setSize(FRAMEWIDTH,FRAMEHEIGHT); srcPane.setDividerLocation(0.5); srcPane.validate(); } public void makeDiffSrcPane(XMLDiffSrcView srcView1, XMLDiffSrcView srcView2) { srcView1.setBackground(Color.lightGray); srcView2.setBackground(Color.lightGray); srcView1.add(new JLabel(filename1,SwingConstants.CENTER),BorderLayout.NORTH); srcView2.add(new JLabel(filename2,SwingConstants.CENTER),BorderLayout.NORTH); JScrollBar vscrollBar = srcView2.getScrollPane().getVerticalScrollBar(); // make the diffSrcView divider fixed. srcView1.getScrollPane().setVerticalScrollBar(vscrollBar); srcView1.getScrollPane().setMinimumSize( new Dimension(FRAMEWIDTH/2,srcView1.getScrollPane().getPreferredSize().height)); srcView2.getScrollPane().setMinimumSize( new Dimension(FRAMEWIDTH/2,srcView2.getScrollPane().getPreferredSize().height)); srcView2.getScrollPane().updateUI(); srcView1.getScrollPane().updateUI(); srcView2.getTextPane().updateUI(); srcView1.getTextPane().updateUI(); srcView2.updateUI(); srcView1.updateUI(); diffSrcPane = new JSplitPane(JSplitPane.HORIZONTAL_SPLIT, srcView1, srcView2); diffSrcPane.setSize(FRAMEWIDTH,FRAMEHEIGHT); diffSrcPane.setDividerLocation(0.5); diffSrcPane.validate(); } public void makeTabbedPane() { tabbedPane = new JTabbedPane(); tabbedPane.addTab("SourceView", null , srcPane, "Source View of Files being Diffed"); tabbedPane.addTab("SourceDiffView", null , diffSrcPane, "Source View of File Diffs"); tabbedPane.addTab("TreeDiffView", null , diffTreePane, "DOM Tree View of File Diffs"); tabbedPane.setSelectedIndex(1); tabbedPane.setSize(FRAMEWIDTH,FRAMEHEIGHT); this.getContentPane().add(tabbedPane); this.setVisible(true); } public void makeXslPane(XMLDocument doc, String title) { xslSrcView = new XMLSourceView(); xslSrcView.setXMLDocument(doc); xslSrcView.setTagForeground(Color.black); xslSrcView.setAttributeValueForeground(Color.black); xslSrcView.setPIDataForeground(Color.black); xslSrcView.setCommentDataForeground(Color.black); xslSrcView.setCDATAForeground(Color.black); xslSrcView.setBackground(Color.lightGray); xslSrcView.getJTextPane().setBackground(Color.white); xslSrcView.add(new JLabel(title,SwingConstants.CENTER), BorderLayout.NORTH); this.enableTransformItem(true); } public void makeResultFilePane(XMLDocument doc) { resultDoc = doc; XMLSourceView resultSrcView = new XMLSourceView(); resultSrcView.setXMLDocument(doc); resultSrcView.setTagForeground(Color.black); resultSrcView.setAttributeValueForeground(Color.black); resultSrcView.setPIDataForeground(Color.black); resultSrcView.setCommentDataForeground(Color.black); resultSrcView.setCDATAForeground(Color.black); resultSrcView.setBackground(Color.lightGray); resultSrcView.getJTextPane().setBackground(Color.white); resultSrcView.add(new JLabel("XSLT Result File",SwingConstants.CENTER), BorderLayout.NORTH); tabbedPane.addTab("ResultSourceView", null , resultSrcView, "Source View of XSLT on File1"); tabbedPane.setSelectedIndex(3); this.enableSaveAsItem(true); } public void makeXslTabbedPane() { tabbedPane = new JTabbedPane(); tabbedPane.addTab("SourceView", null , srcPane, "Source View of XML Files being Diffed"); tabbedPane.addTab("SourceDiffView", null , diffSrcPane, "Source View of File Diffs"); tabbedPane.addTab("XSL Script",null,xslSrcView, "Source View of Diff XSL script"); tabbedPane.setSelectedIndex(2); tabbedPane.setSize(FRAMEWIDTH,FRAMEHEIGHT); this.getContentPane().add(tabbedPane); this.setVisible(true); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) { File selectedFile1, selectedFile2; BufferedReader file1, file2; String arg, temp; if(evt.getSource() instanceof JMenuItem) { arg = evt.getActionCommand(); if(arg.equals("Compare XML Files")) { JFileChooser jFC = new JFileChooser(); jFC.setCurrentDirectory(new File(".")); int retval = jFC.showOpenDialog(this); switch (retval) { case JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION: selectedFile1 = jFC.getSelectedFile(); temp = selectedFile1.getName(); jFC.cancelSelection(); jFC.updateUI(); switch(jFC.showOpenDialog(this)) { case JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION: selectedFile2 = jFC.getSelectedFile(); filename2 = selectedFile2.getName(); filename1 = temp; this.getContentPane().removeAll(); this.enableSaveAsItem(false); mydfApp.showDiffs(selectedFile1, selectedFile2); break; case JFileChooser.CANCEL_OPTION: break; //filename1 = null; // filename1 also null }// switch (jFC.showOpenDialog(this)) break; case JFileChooser.CANCEL_OPTION: break; } }// if(arg.equals("Compare XML Files")) else if(arg.equals("Apply XSL to 1st Input File")) { mydfApp.doXSLTransform(); } else if(arg.equals("Save As")) { JFileChooser jFC = new JFileChooser(); jFC.setCurrentDirectory(new File(".")); int retval = jFC.showOpenDialog(this); if (retval == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) { File file = jFC.getSelectedFile(); try { resultDoc.print(new FileOutputStream(file)); }catch (IOException e) { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "Error:"+e.getMessage(), "XMLDiffer Message", JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE); } } } else if(arg.equals("Exit")) { System.exit(0); } } } public void addTransformMenu() { JMenuItem item; JMenu jmenu = new JMenu("Transform"); item = new JMenuItem("Apply XSL to 1st Input File"); item.addActionListener(this); item.setEnabled(false); jmenu.add(item); this.getJMenuBar().add(jmenu); } protected void enableTransformItem(boolean flag) { this.getJMenuBar().getMenu(1).getItem(0).setEnabled(flag); } protected void enableSaveAsItem(boolean flag) { this.getJMenuBar().getMenu(0).getItem(1).setEnabled(flag); } private void init() { try { this.setTitle("XMLDiffer"); this.getContentPane().setLayout( new BoxLayout(this.getContentPane(),BoxLayout.Y_AXIS)); // make the Differ window non-resizable this.setResizable(false); this.getContentPane().setBackground(SystemColor.control); addMenu(); Dimension screenSize = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize(); Dimension frameSize = this.getSize(); // set Frame size based on screen size such that there is room around it FRAMEWIDTH = screenSize.width - 100; FRAMEHEIGHT = screenSize.height - 200; this.setSize(new Dimension(FRAMEWIDTH, FRAMEHEIGHT)); // put Differ window in the center of the screen this.setLocation((screenSize.width - FRAMEWIDTH)/2, (screenSize.height - FRAMEHEIGHT)/2); this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { System.exit(0); }}); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void addMenu() { JMenuItem item; JMenuBar jmenubar = new JMenuBar(); JMenu jmenu = new JMenu("File"); item = new JMenuItem("Compare XML Files"); item.addActionListener(this); jmenu.add(item); item = new JMenuItem("Save As"); item.addActionListener(this); item.setEnabled(false); jmenu.add(item); jmenu.addSeparator(); item = new JMenuItem("Exit"); item.addActionListener(this); jmenu.add(item); jmenubar.add(jmenu); this.setJMenuBar(jmenubar); } protected static int LEFT_TOP = 0; protected static int RIGHT_TOP = 1; protected static int CENTER = 2; private int FRAMEWIDTH =0; private int FRAMEHEIGHT =0; private XMLDocument resultDoc; private XMLSourceView xslSrcView; private XMLDiffSample mydfApp; private String filename1, filename2; private JTabbedPane tabbedPane; private JSplitPane diffTreePane, srcPane,diffSrcPane; }
|
 Copyright © 2001, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|