Release 2 (9.2)
Part Number A96621-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle9i XML Developer's Kits Guide - XDK Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96621-01 |
|
This chapter contains the following sections:
XML Schema was created by the W3C to describe the content and structure of XML documents in XML. It includes the full capabilities of DTDs (Document Type Descriptions) so that existing DTDs can be converted to XML Schema. XML Schemas have additional capabilities compared to DTDs.
Document Type Definition (DTD) is a mechanism provided by XML 1.0 for declaring constraints on XML markup. DTDs allow the specification of the following:
XML Schema language serves a similar purpose to DTDs, but it is more flexible in specifying XML document constraints and potentially more useful for certain applications. See the following section "DTD Limitations".
Consider the XML document:
<?XML version="1.0"> <publisher pubid="ab1234"> <publish-year>2000</publish-year> <title>The Cat in the Hat</title> <author>Dr. Seuss</author> <artist>Ms. Seuss</artist> <isbn>123456781111</isbn> </publisher>
Consider a typical DTD for the foregoing XML document:
<!ELEMENT publisher (year,title, author+, artist?, isbn)> <!ELEMENT publish-year (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT title (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT author (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT isbn (#PCDATA)> ...
DTDs, also known as XML Markup Declarations, are considered to be deficient in handling certain applications including the following:
DTD limitations include:
Table 6-1, "XML Schema Features" lists XML Schema features. Note that XML Schema features include DTD features.
XML Schema can be used to define a class of XML documents. "Instance document" describes an XML document that conforms to a particular schema.
Although these instances and schemas need not exist specifically as "documents", they are commonly referred to as files. They may exist as any of the following:
Oracle XML Schema Processor for Java has the following features:
XML Schema Processor for Java supports documents in the following encodings:
To run XML Schema Processor for Java, you need the following:
Documentation for Oracle XML Schema Processor for Java is located in the doc/ directory in your install area.
The readme.html file in the root directory of the archive, contains release specific information including bug fixes, and API additions.
Oracle XML Schema Processor is an early adopter release and is written in Java. It includes the production release of the XML Parser for Java v2.
Table 6-2 lists the directory structure after installing XML Schema Processor for Java.
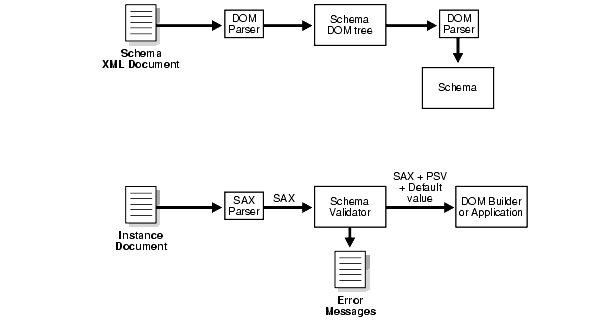
As shown in Figure 6-1, Oracle's XML Schema processor performs two major tasks:
When building the schema, the builder first calls the DOM Parser to parse the schema XML documents into corresponding DOM trees. It then compiles them into an internal schema object. The validator works as a filter between the SAX parser and your applications for the instance document. The validator takes SAX events of the instance document as input and validates them against the schema. If the validator detects any invalid XML component it sends an error message. The output of the validator is:
The XML Parser supports various modes for schema or DTD validation. The setValidationMode method allows different validation parameters to be set. For schema validations, there are these modes available:
schemaLocation and noNamespaceSchemaLocation attributes. See code example XSDSample.java.XSDLax.java.In addition to the validator to build the schema itself, you can use XSDBuilder to build schemas and set it to the validator using setXMLSchema method. See code example XSDSetSchema.java. By using the setXMLSchema method, the validation mode is automatically set to SCHEMA_STRICT_VALIDATION, and both schemaLocation and noNamespaceSchemaLocation attributes are ignored. You can also change the validation mode to SCHEMA_LAX_VALIDATION.
The API of the XML Schema Processor for Java is simple. You can either use either of the following:
setSchemaValidationMode() in the DOMParser as shown in "XML Schema for Java Example 7: XSDSample.java"XSDBuilder and set the schema for XMLParser as shown in"XML Schema for Java Example 8: XSDSetSchema.java".There is no clean-up call similar to xmlclean. If you need to release all memory and reset the state before validating a new XML document, terminate the context and start over.
| See Also:
Oracle9i XML API Reference - XDK and Oracle XML DB, under XDK for Java, XML Schema Processor |
XML Schema Processor for Java directory sample contains sample XML applications that illustrate how to use Oracle XML parser with XML Schema Processor for Java. Here are excerpts from the README file:
The sample Java files provided in this directory are:
XSDSample, a sample driver that processes XML instance documents.
XSDSetSchema, a sample driver to process XML instance documents by overriding the schemaLocation.
XSDLax, based on XSDSetSchema, but uses lax validation mode.
To run the sample program:
make to generate .class files.xmlparserv2.jar, xschema.jar, and the current directory to the CLASSPATH.*.xml files:
java XSDSample report.xml java XSDSetSchema report.xsd report.xml java XSDLax embeded_xsql.xsd embeded_xsql.xml
XML Schema Processor uses the XML Schema specification from report.xsd to validate the contents of report.xml.
catalogue.xml file, as follows:
java XSDSample catalogue.xml java XSDSetSchema cat.xsd catalogue.xml
XML Schema Processor uses the XML Schema specification from cat.xsd to validate the contents of catalogue.xml.
java XSDSample catalogue_e.xml java XSDSample report_e.xml
This is the file Makefile:
# Makefile for sample java files # # If not installed in ORACLE_HOME, set ORACLE_HOME to installation root # # ====================================================================== .SUFFIXES : .java .class CLASSES = XSDSample.class XSDSetSchema.class XSDLax.class # Change it to the appropriate separator based on the OS. PATHSEP = : # Assumes that the CLASSPATH contains JDK classes. MAKE_CLASSPATH = .$(PATHSEP)$(ORACLE_HOME)/lib/xmlparserv2.jar$(PATHSEP)$(ORACLE_HOME)/lib/xschem a.jar$(PATHSEP)$(CLASSPATH) .java.class: @javac -classpath "$(MAKE_CLASSPATH)" $< # make all class files all: $(CLASSES) demo: $(CLASSES) @java -classpath "$(MAKE_CLASSPATH)" XSDSample report.xml > report.out @java -classpath "$(MAKE_CLASSPATH)" XSDSetSchema report.xsd report.xml > report.out @java -classpath "$(MAKE_CLASSPATH)" XSDSample catalogue.xml > catalogue.out @java -classpath "$(MAKE_CLASSPATH)" XSDSetSchema cat.xsd catalogue.xml > catalogue.out @java -classpath "$(MAKE_CLASSPATH)" XSDSample catalogue_e.xml > catalogue_e.out @java -classpath "$(MAKE_CLASSPATH)" XSDSample report_e.xml > report_e.out @java -classpath "$(MAKE_CLASSPATH)" XSDLax embeded_xsql.xsd embeded_xsql.xml> embeded_xsql.out clean: @rm -f *.class @rm -f *.out
This is the sample XML Schema Definition file that supplies input to the XSDSetSchema.java program. XML Schema Processor uses the XML Schema specification from cat.xsd to validate the contents of catalogue.xml.
<?xml version="1.0"?> <schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/10/XMLSchema" targetNamespace="http://www.publishing.org/namespaces/Catalogue" elementFormDefault="qualified" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/1999/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:cat="http://www.publishing.org/namespaces/Catalogue"> <complexType name="PublicationType"> <sequence> <element name="Title" type="string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"/> <element name="Author" type="string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"/> <element name="Date" type="year" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> </sequence> </complexType> <element name="Publication" type="cat:PublicationType" abstract="true"/> <element name="Book" substitutionGroup="cat:Publication"> <complexType> <complexContent> <extension base="cat:PublicationType"> <sequence> <element name="ISBN" type="string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> <element name="Publisher" type="string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> </sequence> </extension> </complexContent> </complexType> </element> <element name="Magazine" substitutionGroup="cat:Publication"> <complexType> <complexContent> <restriction base="cat:PublicationType"> <sequence> <element name="Title" type="string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"/> <element name="Author" type="string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="0"/> <element name="Date" type="year" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> </sequence> </restriction> </complexContent> </complexType> </element> <element name="Catalogue"> <complexType> <sequence> <element ref="cat:Publication" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </schema>
This is the sample XML file that is validated by XML Schema processor against the XML Schema Definition file, cat.xsd, using the program, XSDSetSchema.java.
<?xml version="1.0"?> <Catalogue xmlns="http://www.publishing.org/namespaces/Catalogue" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2000/10/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation= "http://www.publishing.org/namespaces/Catalogue cat.xsd"> <Magazine> <Title>Natural Health</Title> <Date>1999</Date> </Magazine> <Book> <Title>Illusions The Adventures of a Reluctant Messiah</Title> <Author>Richard Bach</Author> <Date>1977</Date> <ISBN>0-440-34319-4</ISBN> <Publisher>Dell Publishing Co.</Publisher> </Book> <Book> <Title>The First and Last Freedom</Title> <Author>J. Krishnamurti</Author> <Date>1954</Date> <ISBN>0-06-064831-7</ISBN> <Publisher>Harper & Row</Publisher> </Book> </Catalogue>
When XML Schema Processor processes this sample XML file using XSDSample.java, it generates XML Schema errors.
<?xml version="1.0"?> <Catalogue xmlns="http://www.publishing.org/namespaces/Catalogue" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2000/10/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation= "http://www.publishing.org/namespaces/Catalogue cat.xsd"> <Magazine> <Title>Natural Health</Title> <Date>1999</Date> </Magazine> <Book> <Title>Illusions The Adventures of a Reluctant Messiah</Title> <Author>Richard Bach</Author> <Date>July 7, 1977</Date> <ISBN>0-440-34319-4</ISBN> <Publisher>Dell Publishing Co.</Publisher> </Book> <Book> <Title>The First and Last Freedom</Title> <Author>J. Krishnamurti</Author> <Date>1954</Date> <ISBN>0-06-064831-7</ISBN> <ISBN>0-06-064831-7</ISBN> <Publisher>Harper & Row</Publisher> </Book> </Catalogue>
This is the sample XML file that is validated by XML Schema processor against the XML Schema Definition file, report.xsd, using the program, XSDSetSchema.java.
<purchaseReport xmlns="http://www.example.com/Report" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.example.com/Report report.xsd" period="P3M" periodEnding="1999-12-31"> <regions> <zip code="95819"> <part number="872-AA" quantity="1"/> <part number="926-AA" quantity="1"/> <part number="833-AA" quantity="1"/> <part number="455-BX" quantity="1"/> </zip> <zip code="63143"> <part number="455-BX" quantity="4"/> </zip> </regions> <parts> <part number="872-AA">Lawnmower</part> <part number="926-AA">Baby Monitor</part> <part number="833-AA">Lapis Necklace</part> <part number="455-BX">Sturdy Shelves</part> </parts> </purchaseReport>
This is the sample XML Schema Definition file that inputs XSDSetSchema.java program. XML Schema Processor uses the XML Schema specification from report.xsd to validate the contents of report.xml.
<schema targetNamespace="http://www.example.com/Report" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:r="http://www.example.com/Report" elementFormDefault="qualified"> <annotation> <documentation xml:lang="en"> Report schema for Example.com Copyright 2000 Example.com. All rights reserved. </documentation> </annotation> <element name="purchaseReport"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="regions" type="r:RegionsType"> <keyref name="dummy2" refer="r:pNumKey"> <selector xpath="r:zip/r:part"/> <field xpath="@number"/> </keyref> </element> <element name="parts" type="r:PartsType"/> </sequence> <attribute name="period" type="duration"/> <attribute name="periodEnding" type="date"/> </complexType> <unique name="dummy1"> <selector xpath="r:regions/r:zip"/> <field xpath="@code"/> </unique> <key name="pNumKey"> <selector xpath="r:parts/r:part"/> <field xpath="@number"/> </key> </element> <complexType name="RegionsType"> <sequence> <element name="zip" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="part" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <complexType> <complexContent> <restriction base="anyType"> <attribute name="number" type="r:SKU"/> <attribute name="quantity" type="positiveInteger"/> </restriction> </complexContent> </complexType> </element> </sequence> <attribute name="code" type="positiveInteger"/> </complexType> </element> </sequence> </complexType> <simpleType name="SKU"> <restriction base="string"> <pattern value="+{3}-[A-Z]{2}"/> </restriction> </simpleType> <complexType name="PartsType"> <sequence> <element name="part" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <complexType> <simpleContent> <extension base="string"> <attribute name="number" type="r:SKU"/> </extension> </simpleContent> </complexType> </element> </sequence> </complexType> </schema>
When XML Schema Processor processes this sample XML file using XSDSample.java, it generates XML Schema errors.
<purchaseReport xmlns="http://www.example.com/Report" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.example.com/Report report.xsd" period="P3M" periodEnding="1999-11-31"> <regions> <zip code="95819"> <part number="872-AA" quantity="1"/> <part number="926-AA" quantity="1"/> <part number="833-AA" quantity="1"/> <part number="455-BX" quantity="1"/> </zip> <zip code="63143"> <part number="455-BX" quantity="4"/> <part number="235-JD" quantity="3"/> </zip> </regions> <parts> <part number="872-AA">Lawnmower</part> <part number="926-AA">Baby Monitor</part> <part number="833-AA">Lapis Necklace</part> <part number="455-BX">Sturdy Shelves</part> </parts> </purchaseReport>
//import oracle.xml.parser.schema.*; import oracle.xml.parser.v2.*; import java.net.*; import java.io.*; import org.w3c.dom.*; import java.util.*; public class XSDSample { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { if (args.length != 1) { System.out.println("Usage: java XSDSample <filename>"); return; } process (args[0]); } public static void process (String xmlURI) throws Exception { DOMParser dp = new DOMParser(); URL url = createURL (xmlURI); // Set Schema Validation to true dp.setValidationMode(XMLParser.SCHEMA_VALIDATION); dp.setPreserveWhitespace (true); dp.setErrorStream (System.out); try { System.out.println("Parsing "+xmlURI); dp.parse (url); System.out.println("The input file <"+xmlURI+"> parsed without errors"); } catch (XMLParseException pe) { System.out.println("Parser Exception: " + pe.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("NonParserException: " + e.getMessage()); } } // Helper method to create a URL from a file name static URL createURL(String fileName) { URL url = null; try { url = new URL(fileName); } catch (MalformedURLException ex) { File f = new File(fileName); try { String path = f.getAbsolutePath(); // This is a bunch of weird code that is required to // make a valid URL on the Windows platform, due // to inconsistencies in what getAbsolutePath returns. String fs = System.getProperty("file.separator"); if (fs.length() == 1) { char sep = fs.charAt(0); if (sep != '/') path = path.replace(sep, '/'); if (path.charAt(0) != '/') path = '/' + path; } path = "file://" + path; url = new URL(path); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { System.out.println("Cannot create url for: " + fileName); System.exit(0); } } return url; } }
When this example is run with cat.xsd and catalogue.xml, XML Schema Processor uses the XML Schema specification from cat.xsd to validate the contents of catalogue.xml.
When this example is run with report.xsd and report.xml, XML Schema Processor uses the XML Schema specification from cat.xsd to validate the contents of report.xml.
import oracle.xml.parser.schema.*; import oracle.xml.parser.v2.*; import java.net.*; import java.io.*; import org.w3c.dom.*; import java.util.*; public class XSDSetSchema { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { if (args.length != 2) { System.out.println("Usage: java XSDSample <schema_file> <xml_file>"); return; } XSDBuilder builder = new XSDBuilder(); URL url = createURL(args[0]); // Build XML Schema Object XMLSchema schemadoc = (XMLSchema)builder.build(url); process(args[1], schemadoc); } public static void process(String xmlURI, XMLSchema schemadoc) throws Exception { DOMParser dp = new DOMParser(); URL url = createURL (xmlURI); // Set Schema Object for Validation dp.setXMLSchema(schemadoc); dp.setValidationMode(XMLParser.SCHEMA_VALIDATION); dp.setPreserveWhitespace (true); dp.setErrorStream (System.out); try { System.out.println("Parsing "+xmlURI); dp.parse (url); System.out.println("The input file <"+xmlURI+"> parsed without errors"); } catch (XMLParseException pe) { System.out.println("Parser Exception: " + pe.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println ("NonParserException: " + e.getMessage()); } } // Helper method to create a URL from a file name static URL createURL(String fileName) { URL url = null; try { url = new URL(fileName); } catch (MalformedURLException ex) { File f = new File(fileName); try { String path = f.getAbsolutePath(); // This is a bunch of weird code that is required to // make a valid URL on the Windows platform, due // to inconsistencies in what getAbsolutePath returns. String fs = System.getProperty("file.separator"); if (fs.length() == 1) { char sep = fs.charAt(0); if (sep != '/') path = path.replace(sep, '/'); if (path.charAt(0) != '/') path = '/' + path; } path = "file://" + path; url = new URL(path); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { System.out.println("Cannot create url for: " + fileName); System.exit(0); } } return url; } }
Here is a listing of XSDLax.java:
import oracle.xml.parser.schema.*; import oracle.xml.parser.v2.*; import java.net.*; import java.io.*; import org.w3c.dom.*; import java.util.*; public class XSDLax { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { if (args.length != 2) { System.out.println("Usage: java XSDSample <schema_file> <xml_file>"); return; } XSDBuilder builder = new XSDBuilder(); URL url = createURL(args[0]); // Build XML Schema Object XMLSchema schemadoc = (XMLSchema)builder.build(url); process(args[1], schemadoc); } public static void process(String xmlURI, XMLSchema schemadoc) throws Exception { DOMParser dp = new DOMParser(); URL url = createURL (xmlURI); // Set Schema Object for Validation dp.setXMLSchema(schemadoc); dp.setValidationMode(XMLParser.SCHEMA_LAX_VALIDATION); dp.setPreserveWhitespace (true); dp.setErrorStream (System.out); try { System.out.println("Parsing "+xmlURI); dp.parse (url); System.out.println("The input file <"+xmlURI+"> parsed without errors"); } catch (XMLParseException pe) { System.out.println("Parser Exception: " + pe.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println ("NonParserException: " + e.getMessage()); } } // Helper method to create a URL from a file name static URL createURL(String fileName) { URL url = null; try { url = new URL(fileName); } catch (MalformedURLException ex) { File f = new File(fileName); try { String path = f.getAbsolutePath(); // This is a bunch of weird code that is required to // make a valid URL on the Windows platform, due // to inconsistencies in what getAbsolutePath returns. String fs = System.getProperty("file.separator"); if (fs.length() == 1) { char sep = fs.charAt(0); if (sep != '/') path = path.replace(sep, '/'); if (path.charAt(0) != '/') path = '/' + path; } path = "file://" + path; url = new URL(path); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { System.out.println("Cannot create url for: " + fileName); System.exit(0); } } return url; } }
This is the input file for XSDLax.java:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns = "http://xmlns.us.oracle.com/XDK/Example/XSQL/schema" targetNamespace = "http://xmlns.us.oracle.com/XDK/Example/XSQL/schema" elementFormDefault="qualified"> <xsd:element name="include-xml"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:simpleContent> <xsd:extension base="xsd:string"> <xsd:attribute name="href" type="xsd:string"/> </xsd:extension> </xsd:simpleContent> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> <xsd:simpleType name="XSQLBool"> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:string"> <xsd:enumeration value="yes"/> <xsd:enumeration value="no"/> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType name="XSQLTagCase"> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:string"> <xsd:enumeration value="lower"/> <xsd:enumeration value="upper"/> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:element name="query"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:simpleContent> <xsd:extension base="xsd:string"> <xsd:attribute name="bind-params" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:attribute name="date-format" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:attribute name="error-statement" type="XSQLBool"/> <xsd:attribute name="fetch-size" type="xsd:positiveInteger"/> <xsd:attribute name="id-attribute" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:attribute name="id-attribute-column" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:attribute name="include-schema" type="XSQLBool"/> <xsd:attribute name="max-rows" type="xsd:positiveInteger"/> <xsd:attribute name="null-indicator" type="XSQLBool"/> <xsd:attribute name="rowset-element" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:attribute name="row-element" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:attribute name="skip-rows" type="xsd:positiveInteger"/> <xsd:attribute name="tag-case" type="XSQLTagCase"/> </xsd:extension> </xsd:simpleContent> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:schema>
Here is the output file from XSDLax.java:
<?xml version="1.0" ?> <page connection="xdkdemo" xmlns:xsql="http://xmlns.us.oracle.com/XDK/Example/XSQL/ schema"> <webpage title=" Search for XDK FAQ"> <search> <xsql:include-xml href="xml/title.xml" /> </search> <content> <question> <xsql:query fetch-size="50" null-indicator="no"> select question from xdkfaq where contains(answer,'{@search}')>0 </xsql:query> </question> <time> <xsql:query tag-case="lower" max-rows="20"> select to_char(sysdate,'DD-MM-YYY') from dual </xsql:query> </time> </content> </webpage> </page>
|
 Copyright © 2001, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|