| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
The floating-point conditions let you determine whether an expression is infinite or is the undefined result of an operation (that is, is not a number or NaN).
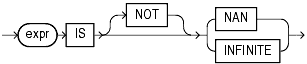
In both forms of floating-point condition, expr must resolve to a numeric datatype or to any datatype that can be implicitly converted to a numeric datatype. Table 6-3 describes the floating-point conditions.
Table 6-3 Floating-Point Conditions
| Type of Condition | Operation | Example |
|---|---|---|
IS [NOT] NAN |
Returns TRUE if expr is the special value NaN when NOT is not specified. Returns TRUE if expr is not the special value NaN when NOT is specified. |
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NAN; |
IS [NOT] INFINITE |
Returns TRUE if expr is the special value +INF or -INF when NOT is not specified. Returns TRUE if expr is neither +INF nor -INF when NOT is specified |
SELECT last_name FROM employees WHERE salary IS NOT INFINITE; |
|
See Also:
|