| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Comparison conditions compare one expression with another. The result of such a comparison can be TRUE, FALSE, or NULL.
Large objects (LOBs) are not supported in comparison conditions. However, you can use PL/SQL programs for comparisons on CLOB data.
When comparing numeric expressions, Oracle uses numeric precedence to determine whether the condition compares NUMBER, BINARY_FLOAT, or BINARY_DOUBLE values. Please refer to "Numeric Precedence " for information on numeric precedence.
Two objects of nonscalar type are comparable if they are of the same named type and there is a one-to-one correspondence between their elements. In addition, nested tables of user-defined object types, even if their elements are comparable, must have MAP methods defined on them to be used in equality or IN conditions.
|
See Also:
|
Table 6-2 lists comparison conditions.
Table 6-2 Comparison Conditions
| Type of Condition | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
= |
Equality test. |
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary = 2500; |
!= ^= < > ¬= |
Inequality test. Some forms of the inequality condition may be unavailable on some platforms. |
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary != 2500; |
> < |
Greater-than and less-than tests. |
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary > 2500; SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary < 2500; |
>= <= |
Greater-than-or-equal-to and less-than-or-equal-to tests. |
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary >= 2500; SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary <= 2500; |
ANY SOME |
Compares a value to each value in a list or returned by a query. Must be preceded by =, !=, >, <, <=, >=. Can be followed by any expression or subquery that returns one or more values.
Evaluates to |
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary = ANY (SELECT salary FROM employees WHERE department_id = 30); |
ALL |
Compares a value to every value in a list or returned by a query. Must be preceded by =, !=, >, <, <=, >=. Can be followed by any expression or subquery that returns one or more values.
Evaluates to |
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary >= ALL ( 1400, 3000); |
A simple comparison condition specifies a comparison with expressions or subquery results.
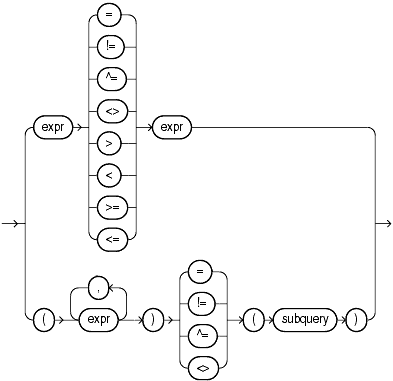
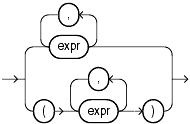
If you use the lower form of this condition (with multiple expressions to the left of the operator), then you must use the lower form of the expression_list, and the values returned by the subquery must match in number and datatype the expressions in expression_list.
|
See Also: "Expression Lists " for more information about combining expressions and SELECT for information about subqueries |
A group comparison condition specifies a comparison with any or all members in a list or subquery.
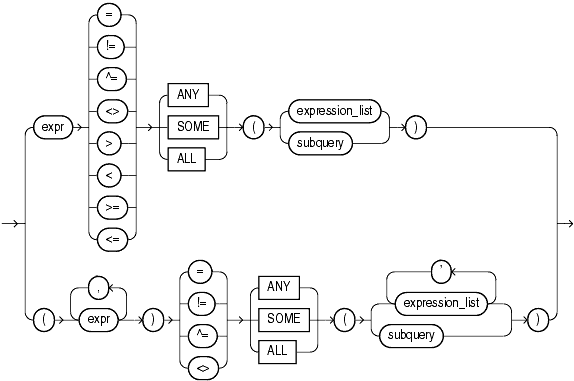

If you use the upper form of this condition (with a single expression to the left of the operator), then you must use the upper form of expression_list. If you use the lower form of this condition (with multiple expressions to the left of the operator), then you must use the lower form of expression_list, and the expressions in each expression_list must match in number and datatype the expressions to the left of the operator.