![]() Secure Global Desktop Administration Guide
> Security
> User prompts and X.509 certificates
Secure Global Desktop Administration Guide
> Security
> User prompts and X.509 certificates
When users log in to a Secure Global Desktop server that has an X.509 certificate, their client
validates the certificate before proceeding. If the certificate is valid and users have
agreed to the initial connection to Secure Global Desktop, the hostname and
the fingerprint of the certificate are added to the hostsvisited file on the client device. The hostsvisited file is
stored in the same location as the user's profile cache.
However, if there are problems with the certificate, for example because the issuer of the certificate is unknown or the certificate has expired, users see a certificate warning message and they are prompted to accept or reject the certificate. This is a potential security risk. How certificate warnings are handled depends on whether or not Secure Global Desktop security services are enabled.
Note Users see prompts about security certificates before agreeing to trust the initial connection to Secure Global Desktop.
When Secure Global Desktop security services are disabled and users see a security warning message about a certificate, the warning message allows users to accept or reject the certificate.
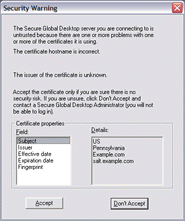
If users accept the certificate and they agree to the connection to the server, the hostname and fingerprint of the certificate are added to the hostsvisited file on the client
device. The certificate is cached for the lifetime of the webtop session. When users next log in, they are not prompted about the certificate.
If users reject the certificate, the connection to Secure Global Desktop is terminated and the certificate details are not added to the hostsvisited file. When users next log in, they are prompted about the certificate.
If users have previously accepted a certificate, or if the only error with the certificate is that the issuer is unknown, then users are not prompted about the certificate.
When Secure Global Desktop security services are enabled and users see a security warning message about a certificate, the warning message allows users to accept the certificate permanently or temporarily, or to reject the certificate.

If users accept the certificate temporarily and they agree to the connection to the server, the hostname and fingerprint of the certificate are
added to the hostsvisited file on the client device. The certificate is cached for the lifetime of the webtop session. When users
next log in, they are prompted about the certificate.
If users accept the certificate permanently and they agree to the connection to the server, the hostname and fingerprint of the certificate are added to the hostsvisited file
on the client device. The certificate is also added to the certstore.pem file on the client device.
The certstore.pem file is stored in the same location as the user's profile
cache. Users can choose to accept just the certificate or the certificate and its chain.
When users next log in, they are not prompted about the certificate.
If users reject the certificate, the connection to Secure Global Desktop is terminated and no certificate details are added to the
hostsvisited file. When users next log in, they are prompted about the certificate.
In a default installation, Secure Global Desktop supports X.509 certificates that have been signed by a number of Certificate Authorities.
You can use any other type of Base 64-encoded PEM-format X.509 certificate. However, these certificates cannot be validated unless you install the Certificate Authority (CA) certificate (or root certificate) that was used to sign that certificate. If you do not install the CA certificate, users see an issuer unknown error and are prompted to accept or reject the certificate.
Copyright © 1997-2006 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.