| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28286-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28286-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Purpose
Use the ALTER INDEXTYPE statement to add or drop an operator of the indextype or to modify the implementation type or change the properties of the indextype.
Prerequisites
The indextype must be in your own schema or you must have the ALTER ANY INDEXTYPE system privilege.
To add a new operator, you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the operator.
To change the implementation type, you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the new implementation type.
Syntax
alter_indextype::=
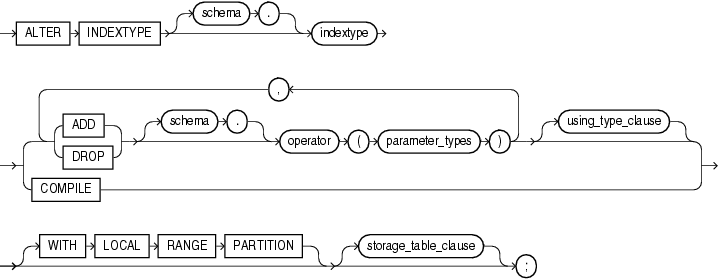
(using_type_clause::=, storage_table_clause)
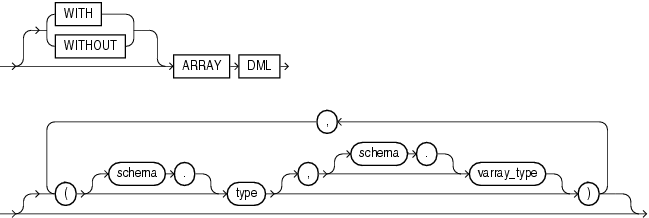
array_DML_clause ::=

Semantics
schema
Specify the name of the schema in which the indextype resides. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database assumes the indextype is in your own schema.
indextype
Specify the name of the indextype to be modified.
Use the ADD or DROP clause to add or drop an operator.
No special privilege needed to drop.
For schema, specify the schema containing the operator. If you omit schema, then Oracle assumes the operator is in your own schema.
For operator, specify the name of the operator supported by the indextype.
All the operators listed in this clause must be valid operators.
For parameter_type, list the types of parameters to the operator.
The USING clause lets you specify a new type to provide the implementation for the indextype.
Use this clause to modify the indextype to support the array interface for the ODCIIndexInsert method.
type and varray_type If the datatype of the column to be indexed is a user-defined object type, then you must specify this clause to identify the varray varray_type that Oracle should use to hold column values of type. If the indextype supports a list of types, then you can specify a corresponding list of varray types. If you omit schema for either type or varray_type, then Oracle assumes the type is in your own schema.
If the datatype of the column to be indexed is a built-in system type, then any varray type specified for the indextype takes precedence over the ODCI types defined by the system.
COMPILE
Use this clause to recompile the indextype explicitly. This clause is required only after some upgrade operations, because Oracle Database normally recompiles the indextype automatically.
storage_table_clause
This clause has the same behavior when altering an indextype that it has when you are creating an indextype. Refer to the CREATE INDEXTYPE storage_table_clause for more information.
WITH LOCAL RANGE PARTITION
This clause has the same behavior when altering an indextype that it has when you create an indextype. Refer to the CREATE INDEXTYPE clause WITH LOCAL RANGE PARTITION for more information.
Example
Altering an Indextype: Example The following example compiles the position_indextype indextype created in "Creating an Indextype: Example".
ALTER INDEXTYPE position_indextype COMPILE;