| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28286-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28286-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Syntax
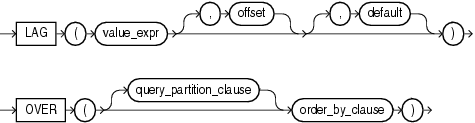
See Also:
"Analytic Functions" for information on syntax, semantics, and restrictions, including valid forms ofvalue_exprPurpose
LAG is an analytic function. It provides access to more than one row of a table at the same time without a self join. Given a series of rows returned from a query and a position of the cursor, LAG provides access to a row at a given physical offset prior to that position.
If you do not specify offset, then its default is 1. The optional default value is returned if the offset goes beyond the scope of the window. If you do not specify default, then its default is null.
You cannot nest analytic functions by using LAG or any other analytic function for value_expr. However, you can use other built-in function expressions for value_expr.
Examples
The following example provides, for each salesperson in the employees table, the salary of the employee hired just before:
SELECT last_name, hire_date, salary, LAG(salary, 1, 0) OVER (ORDER BY hire_date) AS prev_sal FROM employees WHERE job_id = 'PU_CLERK' ORDER BY last_name, hire_date, salary, prev_sal; LAST_NAME HIRE_DATE SALARY PREV_SAL ------------------------- --------- ---------- ---------- Baida 24-DEC-97 2900 2800 Colmenares 10-AUG-99 2500 2600 Himuro 15-NOV-98 2600 2900 Khoo 18-MAY-95 3100 0 Tobias 24-JUL-97 2800 3100