| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
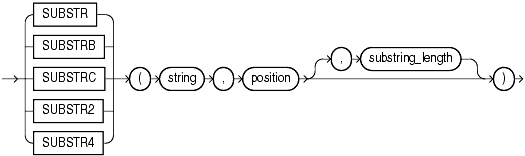
The SUBSTR functions return a portion of string, beginning at character position, substring_length characters long. SUBSTR calculates lengths using characters as defined by the input character set. SUBSTRB uses bytes instead of characters. SUBSTRC uses Unicode complete characters. SUBSTR2 uses UCS2 code points. SUBSTR4 uses UCS4 code points.
If position is 0, then it is treated as 1.
If position is positive, then Oracle Database counts from the beginning of string to find the first character.
If position is negative, then Oracle counts backward from the end of string.
If substring_length is omitted, then Oracle returns all characters to the end of string. If substring_length is less than 1, then Oracle returns null.
string can be any of the datatypes CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB. Both position and substring_length must be of datatype NUMBER, or any datatype that can be implicitly converted to NUMBER, and must resolve to an integer. The return value is the same datatype as string. Floating-point numbers passed as arguments to SUBSTR are automatically converted to integers.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Globalization Support Guide for more information aboutSUBSTR functions and length semantics in different locales |
The following example returns several specified substrings of "ABCDEFG":
SELECT SUBSTR('ABCDEFG',3,4) "Substring"
FROM DUAL;
Substring
---------
CDEF
SELECT SUBSTR('ABCDEFG',-5,4) "Substring"
FROM DUAL;
Substring
---------
CDEF
Assume a double-byte database character set:
SELECT SUBSTRB('ABCDEFG',5,4.2) "Substring with bytes"
FROM DUAL;
Substring with bytes
--------------------
CD